Dimerization of the papillomavirus E2 protein is required for efficient mitotic chromosome association and Brd4 binding
- PMID: 18495759
- PMCID: PMC2493320
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00772-08
Dimerization of the papillomavirus E2 protein is required for efficient mitotic chromosome association and Brd4 binding
Abstract
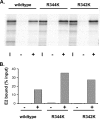
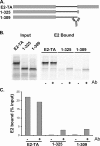
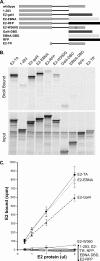
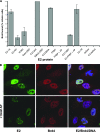
The E2 proteins of several papillomaviruses link the viral genome to mitotic chromosomes to ensure retention and the efficient partitioning of genomes into daughter cells following cell division. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 binds to chromosomes in a complex with Brd4, a cellular bromodomain protein. Interaction with Brd4 is also important for E2-mediated transcriptional regulation. The transactivation domain of E2 is crucial for interaction with the Brd4 protein; proteins lacking or mutated in this domain do not interact with Brd4. However, we found that the C-terminal DNA binding/dimerization domain of E2 is also required for efficient binding to Brd4. Mutations that eliminated the DNA binding function of E2 had no effect on the ability of E2 to interact with Brd4, but an E2 protein with a mutation that disrupted C-terminal dimerization bound Brd4 with greatly reduced efficiency. Furthermore, E2 proteins in which the C-terminal domains were replaced with the dimeric DNA binding domain of EBNA-1 or Gal4 bound efficiently to the Brd4 protein, but the replacement of the E2 C-terminal domain with a monomeric red fluorescent protein did not rescue efficient Brd4 binding. Thus, E2 bound to Brd4 most efficiently as a dimer. To prove this finding further, the E2 DNA binding domain was replaced with an FKBP12-derived domain in which dimerization was regulated by a bivalent ligand. This fusion protein bound Brd4 efficiently only in the presence of the ligand, confirming that a dimer of E2 was required. Correspondingly, E2 proteins that could dimerize were able to bind to mitotic chromosomes much more efficiently than monomeric E2 polypeptides.
Figures

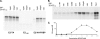
References
-
- Abbate, E. A., C. Voitenleitner, and M. R. Botchan. 2006. Structure of the papillomavirus DNA-tethering complex E2:Brd4 and a peptide that ablates HPV chromosomal association. Mol. Cell 24877-889. - PubMed
-
- Androphy, E. J., D. R. Lowy, and J. T. Schiller. 1987. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature 32570-73. - PubMed
-
- Antson, A. A., J. E. Burns, O. V. Moroz, D. J. Scott, C. M. Sanders, I. B. Bronstein, G. G. Dodson, K. S. Wilson, and N. J. Maitland. 2000. Structure of the intact transactivation domain of the human papillomavirus E2 protein. Nature 403805-809. - PubMed
-
- Bastien, N., and A. A. McBride. 2000. Interaction of the papillomavirus E2 with mitotic chromosomes. Virology 270124-134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

