Protein kinase B/Akt activity is involved in renal TGF-beta1-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 18495798
- PMCID: PMC2494512
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00548.2007
Protein kinase B/Akt activity is involved in renal TGF-beta1-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
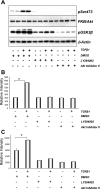
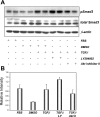
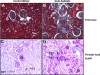
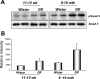
The molecular pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy (DN), the leading cause of end-stage renal disease worldwide, is complex and not fully understood. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1) plays a critical role in many fibrotic disorders, including DN. In this study, we report protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) activation as a downstream event contributing to the pathophysiology of DN. We investigated the potential of PKB/Akt to mediate the profibrotic bioactions of TGF-beta1 in kidney. Treatment of normal rat kidney epithelial cells (NRK52E) with TGF-beta1 resulted in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and PKB/Akt as evidenced by increased Ser473 phosphorylation and GSK-3beta phosphorylation. TGF-beta1 also stimulated increased Smad3 phosphorylation in these cells, a response that was insensitive to inhibition of PI3K or PKB/Akt. NRK52E cells displayed a loss of zona occludins 1 and E-cadherin and a gain in vimentin and alpha-smooth muscle actin expression, consistent with the fibrotic actions of TGF-beta1. These effects were blocked with inhibitors of PI3K and PKB/Akt. Furthermore, overexpression of PTEN, the lipid phosphatase regulator of PKB/Akt activation, inhibited TGF-beta1-induced PKB/Akt activation. Interestingly, in the Goto-Kakizaki rat model of type 2 diabetes, we also detected increased phosphorylation of PKB/Akt and its downstream target, GSK-3beta, in the tubules, relative to that in control Wistar rats. Elevated Smad3 phosphorylation was also detected in kidney extracts from Goto-Kakizaki rats with chronic diabetes. Together, these data suggest that TGF-beta1-mediated PKB/Akt activation may be important in renal fibrosis during diabetic nephropathy.
Figures






References
-
- Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK, Arteaga CL. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for TGFβ-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J Cell Sci 115: 3193–3206, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses HL, Arteaga CL. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem 275: 36803–36810, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Garcia De Herreros A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2: 84–89, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

