Central infusion of aldosterone synthase inhibitor prevents sympathetic hyperactivity and hypertension by central Na+ in Wistar rats
- PMID: 18495825
- PMCID: PMC2494821
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.90352.2008
Central infusion of aldosterone synthase inhibitor prevents sympathetic hyperactivity and hypertension by central Na+ in Wistar rats
Abstract
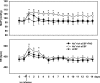
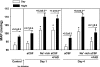
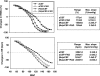
In Wistar rats, increasing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Na+ concentration ([Na+]) by intracerebroventricular (ICV) infusion of hypertonic saline causes sympathetic hyperactivity and hypertension that can be prevented by blockade of brain mineralocorticoid receptors (MR). To assess the role of aldosterone produced locally in the brain in the activation of MR in the central nervous system (CNS), Wistar rats were infused ICV with artificial CSF (aCSF), Na+ -rich (800 mmol/l) aCSF, aCSF plus the aldosterone synthase inhibitor FAD286 (100 microg x kg(-1) x day(-1)), or Na+ -rich aCSF plus FAD286. After 2 wk of infusion, rats treated with Na+ -rich aCSF exhibited significant increases in aldosterone and corticosterone content in the hypothalamus but not in the hippocampus, as well as increases in resting blood pressure (BP) and sympathoexcitatory responses to air stress, and impairment of arterial baroreflex function. Concomitant ICV infusion of FAD286 prevented the Na+ -induced increase in hypothalamic aldosterone but not corticosterone and prevented most of the increases in resting BP and sympathoexcitatory and pressor responses to air stress and the baroreflex impairment. FAD286 had no effects in rats infused with ICV aCSF. In another set of rats, 24-h BP and heart rate were recorded via telemetry before and during a 14-day ICV infusion of Na+ -rich aCSF with or without FAD286. Na+ -rich aCSF without FAD286 caused sustained increases ( approximately 10 mmHg) in resting mean arterial pressure that were absent in the rats treated with FAD286. These data suggest that in Wistar rats, an increase in CSF [Na+] may increase the biosynthesis of corticosterone and aldosterone in the hypothalamus, and mainly aldosterone activates MR in the CNS leading to sympathetic hyperactivity and hypertension.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of central nervous system aldosterone synthase and mineralocorticoid receptors in salt-induced hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):R994-R1000. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90903.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19118098
-
Activation of brain renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system by central sodium in Wistar rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Sep;291(3):H1109-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00024.2006. Epub 2006 Apr 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16603700
-
Role of brain corticosterone and aldosterone in central angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Hypertension. 2013 Sep;62(3):564-71. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01557. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23856493
-
The central role of the brain aldosterone-"ouabain" pathway in salt-sensitive hypertension.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1802(12):1132-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.03.004. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20230892 Review.
-
Mineralocorticoid actions in the brain and hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2011 Jun;13(3):214-20. doi: 10.1007/s11906-011-0192-0. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2011. PMID: 21298576 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel therapeutic targets for hypertension.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 Aug;7(8):431-41. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.85. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20567239 Review.
-
Actions of aldosterone in the cardiovascular system: the good, the bad, and the ugly?Pflugers Arch. 2009 Jun;458(2):231-46. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0616-0. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 19018562
-
Neuroendocrine humoral and vascular components in the pressor pathway for brain angiotensin II: a new axis in long term blood pressure control.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 2;9(9):e108916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108916. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25275393 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Renin-Angiotensin system and aldosterone on cardiometabolic syndrome.Int J Hypertens. 2011;2011:685238. doi: 10.4061/2011/685238. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Int J Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21785705 Free PMC article.
-
New agents modulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system-Will there be a new therapeutic option?Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Nov;241(17):1888-1899. doi: 10.1177/1535370216660211. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27439538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arriza JL, Weinberger C, Cerelli G, Glaser TM, Handelin BL, Housman DE, Evans RM. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science 237: 268–275, 1987. - PubMed
-
- Bligh-Tynan ME, Bhagwat SA, Castonguay TW. The effects of chronic cold exposure on diurnal corticosterone and aldosterone rhythms in Sprague-Dawley rats. Physiol Behav 54: 363–367, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Bunag RD, Miyajima E. Sympathetic hyperactivity elevates blood pressure during acute cerebroventricular infusion of hypertonic salt in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6: 844–851, 1984. - PubMed
-
- DiBona GF, Jones SY, Brooks VL. ANG II receptor blockade and arterial baroreflex regulation of renal nerve activity in cardiac failure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 269: R1189–R1196, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Fiebeler A, Nussberger J, Shagdarsuren E, Rong S, Hilfenhaus G, Al-Saadi N, Dechend R, Wellner M, Meiners S, Maser-Gluth C, Jeng AY, Webb RL, Luft FC, Muller DN. Aldosterone synthase inhibitor ameliorates angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circulation 111: 3087–3094, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

