Aquaporin-4-deficient mice have increased extracellular space without tortuosity change
- PMID: 18495879
- PMCID: PMC2659334
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0257-08.2008
Aquaporin-4-deficient mice have increased extracellular space without tortuosity change
Abstract
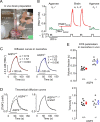
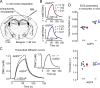
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is the major water channel expressed at fluid-tissue barriers throughout the brain and plays a crucial role in cerebral water balance. To assess whether these channels influence brain extracellular space (ECS) under resting physiological conditions, we used the established real-time iontophoresis method with tetramethylammonium (TMA(+)) to measure three diffusion parameters: ECS volume fraction (alpha), tortuosity (lambda), and TMA(+) loss (k'). In vivo measurements were performed in the somatosensory cortex of AQP4-deficient (AQP4(-/-)) mice and wild-type controls with matched age. Mice lacking AQP4 showed a 28% increase in alpha (0.23 +/- 0.007 vs 0.18 +/- 0.003) with no differences in lambda (1.62 +/- 0.04 vs 1.61 +/- 0.02) and k' (0.0045 +/- 0.0001 vs 0.0031 +/- 0.0009 s(-1)). Additional recordings in brain slices showed similarly elevated alpha in AQP4(-/-) mice, and no differences in lambda and k' between the two genotypes. This is the first direct comparison of ECS properties in adult mice lacking AQP4 water channels with wild-type animals and demonstrates a significant enlargement of the volume fraction but no difference in hindrance to TMA(+) diffusion, expressed as tortuosity. These findings provide direct evidence for involvement of AQP4 in modulation of the ECS volume fraction and provide a basis for future modeling of water and ion transport in the CNS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of alpha-syntrophin deletion on the changes in tissue structure and extracellular diffusion associated with cell swelling under physiological and pathological conditions.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 5;8(7):e68044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068044. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861848 Free PMC article.
-
Enlarged extracellular space of aquaporin-4-deficient mice does not enhance diffusion of Alexa Fluor 488 or dextran polymers.Neuroscience. 2009 Jun 16;161(1):39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.017. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19303428 Free PMC article.
-
The role of aquaporin-4 and transient receptor potential vaniloid isoform 4 channels in the development of cytotoxic edema and associated extracellular diffusion parameter changes.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Jul;50(1):1685-1699. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14338. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30633415
-
Diffusion in brain extracellular space.Physiol Rev. 2008 Oct;88(4):1277-340. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2007. Physiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18923183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of dead-space microdomains to tortuosity of brain extracellular space.Neurochem Int. 2004 Sep;45(4):467-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2003.11.011. Neurochem Int. 2004. PMID: 15186912 Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocyte-neuron circuits in epilepsy.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Apr;179:106058. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106058. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 36868484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronan deficiency due to Has3 knock-out causes altered neuronal activity and seizures via reduction in brain extracellular space.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 30;34(18):6164-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3458-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24790187 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of alpha-syntrophin deletion on the changes in tissue structure and extracellular diffusion associated with cell swelling under physiological and pathological conditions.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 5;8(7):e68044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068044. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861848 Free PMC article.
-
Brain water mobility decreases after astrocytic aquaporin-4 inhibition using RNA interference.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Mar;31(3):819-31. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.163. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011. PMID: 20877385 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of aquaporin-4 deficiency in a mouse model of severe global cerebral ischemia produced by transient 4-vessel occlusion.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jun 27;574:70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.03.073. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24717641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Williamson A, Palomba M, Eid T, de Lanerolle NC, Nagelhus EA, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Agre P, Ottersen OP. Delayed K+ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: phenotypic defects in brains of alpha-syntrophin-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:13615–13620. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anděrová M, Kubinová S, Mazel T, Chvátal A, Eliasson C, Pekny M, Syková E. Effect of elevated K+, hypotonic stress, and cortical spreading depression on astrocyte swelling in GFAP-deficient mice. Glia. 2001;35:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Binder DK, Oshio K, Ma T, Verkman AS, Manley GT. Increased seizure threshold in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. NeuroReport. 2004a;15:259–262. - PubMed
-
- Binder DK, Yao X, Zador Z, Sick TJ, Verkman AS, Manley GT. Increased seizure duration and slowed potassium kinetics in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Glia. 2006;53:631–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
