A specific CD36-dependent signaling pathway is required for platelet activation by oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- PMID: 18497330
- PMCID: PMC2749986
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.172064
A specific CD36-dependent signaling pathway is required for platelet activation by oxidized low-density lipoprotein
Abstract
Platelet hyperactivity associated with hyperlipidemia may contribute to development of a prothrombotic state. We previously showed that oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) formed in the setting of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis activated platelets in a CD36-dependent manner. We now show that mitogen-activated protein kinase c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)2 and its upstream activator MKK4 were phosphorylated in platelets exposed to oxLDL. Using apoE(-/-) mice as a model of hyperlipidemia, we showed that JNK was constitutively phosphorylated in platelets in a CD36-dependent manner. Inhibition of src kinase activity reduced JNK phosphorylation by oxLDL. Immunoprecipitations revealed that active phosphorylated forms of src kinases Fyn and Lyn were recruited to CD36 in platelets exposed to oxLDL. Pharmacological inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase JNK or src family kinases abolished platelet activation by oxLDL in vitro. Using a murine carotid artery thrombosis model we demonstrated CD36-dependent phosphorylation of platelet JNK within thrombi. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition of JNK prolonged thrombosis times in wild-type but not cd36-null mice in vivo. These findings suggest that a specific CD36-dependent signaling pathway is required for platelet activation by oxLDL and may provide insights related to development of novel antiplatelet therapies more relevant to atherothrombosis than to normal hemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: None.
Figures

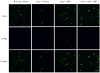



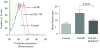
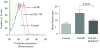
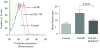


References
-
- Knowles DM, 2nd, Tolidjian B, Marboe C, D'Agati V, Grimes M, Chess L. Monoclonal anti-human monocyte antibodies OKM1 and OKM5 possess distinctive tissue distributions including differential reactivity with vascular endothelium. J Immunol. 1984;132:2170–2173. - PubMed
-
- Rhinehart-Jones T, Greenwalt DE. A detergent-sensitive 113-kDa conformer/complex of CD36 exists on the platelet surface. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 1996;326:115–118. - PubMed
-
- Abumrad NA, el-Maghrabi MR, Amri EZ, Lopez E, Grimaldi PA. Cloning of a rat adipocyte membrane protein implicated in binding or transport of long-chain fatty acids that is induced during preadipocyte differentiation. Homology with human CD36. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1993;268:17665–17668. - PubMed
-
- Van Nieuwenhoven FA, Verstijnen CP, Abumrad NA, Willemsen PH, Van Eys GJ, Van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JF. Putative membrane fatty acid translocase and cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding protein are co-expressed in rat heart and skeletal muscles. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 1995;207:747–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

