A mutation (R826W) in nucleotide-binding domain 1 of ABCC8 reduces ATPase activity and causes transient neonatal diabetes
- PMID: 18497752
- PMCID: PMC2475326
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2008.71
A mutation (R826W) in nucleotide-binding domain 1 of ABCC8 reduces ATPase activity and causes transient neonatal diabetes
Abstract
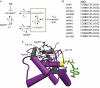
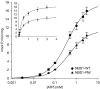
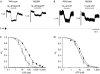
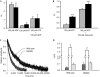
Activating mutations in the pore-forming Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and regulatory sulphonylurea receptor SUR1 (ABCC8) subunits of the K(ATP) channel are a common cause of transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM). We identified a new TNDM mutation (R826W) in the first nucleotide-binding domain (NBD1) of SUR1. The mutation was found in a region that heterodimerizes with NBD2 to form catalytic site 2. Functional analysis showed that this mutation decreases MgATP hydrolysis by purified maltose-binding protein MBP-NBD1 fusion proteins. Inhibition of ATP hydrolysis by MgADP or BeF was not changed. The results indicate that the ATPase cycle lingers in the post-hydrolytic MgADP.P(i)-bound state, which is associated with channel activation. The extent of MgADP-dependent activation of K(ATP) channel activity was unaffected by the R826W mutation, but the time course of deactivation was slowed. Channel inhibition by MgATP was reduced, leading to an increase in resting whole-cell currents. In pancreatic beta cells, this would lead to less insulin secretion and thereby diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ashcroft FM (2007) The Walter B Cannon Lecture. ATP-sensitive K-channels and disease: from molecule to malady. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293: E880–E889 - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22: 3099–3108 - PubMed
-
- Dawson RJ, Locher KP (2006) Structure of a bacterial multidrug ABC transporter. Nature 443: 156–157
-
- de Wet H, Rees M, Shimomura K, Aittoniemi J, Patch AM, Flanagan S, Ellard S, Hattersley AT, Sansom MSP, Ashcroft FM (2007a) Increased ATP-ase activity produced by mutations at R1380 in nucleotide-binding domain 2 of ABCC8 causes neonatal diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 18988–18992 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

