Proteasome subunit Rpn13 is a novel ubiquitin receptor
- PMID: 18497817
- PMCID: PMC2839886
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06926
Proteasome subunit Rpn13 is a novel ubiquitin receptor
Abstract
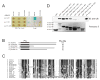
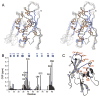
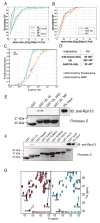
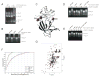
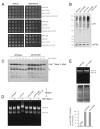
Proteasomal receptors that recognize ubiquitin chains attached to substrates are key mediators of selective protein degradation in eukaryotes. Here we report the identification of a new ubiquitin receptor, Rpn13/ARM1, a known component of the proteasome. Rpn13 binds ubiquitin through a conserved amino-terminal region termed the pleckstrin-like receptor for ubiquitin (Pru) domain, which binds K48-linked diubiquitin with an affinity of approximately 90 nM. Like proteasomal ubiquitin receptor Rpn10/S5a, Rpn13 also binds ubiquitin-like (UBL) domains of UBL-ubiquitin-associated (UBA) proteins. In yeast, a synthetic phenotype results when specific mutations of the ubiquitin binding sites of Rpn10 and Rpn13 are combined, indicating functional linkage between these ubiquitin receptors. Because Rpn13 is also the proteasomal receptor for Uch37, a deubiquitinating enzyme, our findings suggest a coupling of chain recognition and disassembly at the proteasome.
Figures
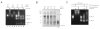
Comment in
-
Cell biology: two hands for degradation.Nature. 2008 May 22;453(7194):460-1. doi: 10.1038/453460a. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18497808 No abstract available.
References
-
- Voges D, Zwickl P, Baumeister W. The 26S proteasome: a molecular machine designed for controlled proteolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:1015–68. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux Q, Ustrell V, Pickart C, Rechsteiner M. A 26 S protease subunit that binds ubiquitin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:7059–61. - PubMed
-
- Elsasser S, Chandler-Militello D, Muller B, Hanna J, Finley D. Rad23 and Rpn10 serve as alternative ubiquitin receptors for the proteasome. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:26817–22. - PubMed
-
- Verma R, Oania R, Graumann J, Deshaies RJ. Multiubiquitin chain receptors define a layer of substrate selectivity in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Cell. 2004;118:99–110. - PubMed
-
- Elsasser S, Finley D. Delivery of ubiquitinated substrates to protein-unfolding machines. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:742–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

