The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid beta accumulation in mice
- PMID: 18497889
- PMCID: PMC2391284
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI33585
The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid beta accumulation in mice
Abstract
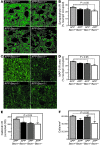
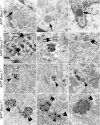
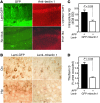
Autophagy is the principal cellular pathway for degradation of long-lived proteins and organelles and regulates cell fate in response to stress. Recently, autophagy has been implicated in neurodegeneration, but whether it is detrimental or protective remains unclear. Here we report that beclin 1, a protein with a key role in autophagy, was decreased in affected brain regions of patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) early in the disease process. Heterozygous deletion of beclin 1 (Becn1) in mice decreased neuronal autophagy and resulted in neurodegeneration and disruption of lysosomes. In transgenic mice that express human amyloid precursor protein (APP), a model for AD, genetic reduction of Becn1 expression increased intraneuronal amyloid beta (Abeta) accumulation, extracellular Abeta deposition, and neurodegeneration and caused microglial changes and profound neuronal ultrastructural abnormalities. Administration of a lentiviral vector expressing beclin 1 reduced both intracellular and extracellular amyloid pathology in APP transgenic mice. We conclude that beclin 1 deficiency disrupts neuronal autophagy, modulates APP metabolism, and promotes neurodegeneration in mice and that increasing beclin 1 levels may have therapeutic potential in AD.
Figures
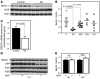
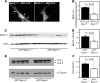
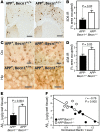
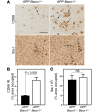
Comment in
-
Regulation of Abeta pathology by beclin 1: a protective role for autophagy?J Clin Invest. 2008 Jun;118(6):2015-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI35662. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18497881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levine B. Eating oneself and uninvited guests: autophagy-related pathways in cellular defense. Cell. 2005;120:159–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG10435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084254/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020603/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA84254/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG20603/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG02270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG22074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG5131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG010435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG18440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

