DLC1 suppresses distant dissemination of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in nude mice through reduction of RhoA GTPase activity, actin cytoskeletal disruption and down-regulation of genes involved in metastasis
- PMID: 18497990
- PMCID: PMC7185305
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo_32_6_1285
DLC1 suppresses distant dissemination of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in nude mice through reduction of RhoA GTPase activity, actin cytoskeletal disruption and down-regulation of genes involved in metastasis
Abstract
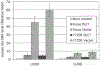
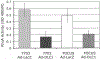
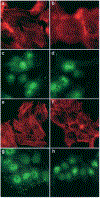
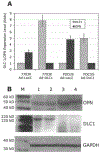
The process of cell dissemination from the primary tumors to distant sites is the most harmful event during cancer progression, and the leading cause of cancer death. We have previously demonstrated that restoration of DLC1 tumor suppressor gene expression in the DLC1-negative Focus and 7703K human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines induced caspase-3 mediated apoptosis, reduced cell growth in vitro and tumorigenicity in vivo and diminished the ability to migrate through Matrigel, a property suggestive of metastatic potential in vivo. We now show that subcutaneous tumors developing after inoculation of Focus and 7703K cells into nude mice disseminate cells to liver and lung, and this process is markedly suppressed by restoration of DLC1 expression. Inhibition of tumor cell dissemination was associated with lower levels of RhoA activity, an increase in rounded cells and a reduction in actin stress fibers and focal adhesion molecules that are of critical importance in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. In addition, DLC1 down-regulated the expression of osteopontin and matrix metalloproteinase-9, which are highly up-regulated in most primary HCC with associated metastases. These observations implicate the DLC1 gene in suppression of HCC cell dissemination and identify novel cellular and genetic alterations that contribute to prevention of metastasis, a life-threatening event in cancer progression.
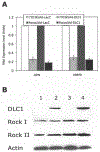
Figures
References
-
- Weinberg RA: Moving out: invasion and metastasis In: The Biology of Cancer. Garland Science, Taylor & Francis Group, LLC; New York, pp 587–655, 2007.
-
- Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES and Hynes RO: Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 406: 532–535, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DX and Massague J: Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Genet 8: 341–352, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Yuan BZ, Miller MJ, Keck CL, Zimonjic D, Thorgeirsson SS and Popescu NC: Cloning, characterization and chromosomal localization of a gene frequently deleted in human liver cancer (DLC-1) homogous to rat RhoGAP. Cancer Res 58: 2196–2199, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

