Liquid crystalline phase of G-tetrad DNA for NMR study of detergent-solubilized proteins
- PMID: 18498162
- PMCID: PMC2652356
- DOI: 10.1021/ja801729f
Liquid crystalline phase of G-tetrad DNA for NMR study of detergent-solubilized proteins
Abstract
The liquid crystalline phase consisting of the potassium salt of the dinucleotide d(GpG) is compatible with detergents commonly used for solubilizing membrane proteins, including dodecylphosphocholine, the lysolipid 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, and small bicelles consisting of dihexanoyl phosphatidylcholine and dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. The chiral nematic liquid crystalline phase of d(GpG) consists of long columns of stacked G-tetrad structures and carry a net negative charge. For water-soluble systems, the protein alignment induced by d(GpG) is very similar to that observed for liquid crystalline Pf1 bacteriophage, but of opposite sign. Alignment of the detergent-solubilized fusion domain of hemagglutinin is demonstrated to be homogeneous and stable, resulting in high quality NMR spectra suitable for the measurement of residual dipolar couplings.
Figures
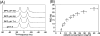

Similar articles
-
Modulating alignment of membrane proteins in liquid-crystalline and oriented gel media by changing the size and charge of phospholipid bicelles.J Biomol NMR. 2013 Apr;55(4):369-77. doi: 10.1007/s10858-013-9720-3. Epub 2013 Mar 19. J Biomol NMR. 2013. PMID: 23508769 Free PMC article.
-
Designing DNA Nanotube Liquid Crystals as a Weak-Alignment Medium for NMR Structure Determination of Membrane Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1500:203-215. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6454-3_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27813010
-
A Positively Charged Liquid Crystalline Medium for Measuring Residual Dipolar Couplings in Membrane Proteins by NMR.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Sep 23;137(37):11932-4. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07515. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 26348133
-
Short-chain phospholipids as detergents.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Nov 23;1508(1-2):164-81. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4157(00)00008-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11090824 Review.
-
Deuterated detergents for structural and functional studies of membrane proteins: Properties, chemical synthesis and applications.Mol Membr Biol. 2015 Aug-Dec;32(5-8):139-55. doi: 10.3109/09687688.2015.1125536. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Mol Membr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26906947 Review.
Cited by
-
Solution structure of yeast Rpn9: insights into proteasome lid assembly.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):6878-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.626762. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25631053 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-induced alignment of membrane proteins enables the measurement and structural analysis of residual dipolar couplings with dipolar waves and lambda-maps.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Oct 14;131(40):14140-1. doi: 10.1021/ja905640d. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19761238 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating alignment of membrane proteins in liquid-crystalline and oriented gel media by changing the size and charge of phospholipid bicelles.J Biomol NMR. 2013 Apr;55(4):369-77. doi: 10.1007/s10858-013-9720-3. Epub 2013 Mar 19. J Biomol NMR. 2013. PMID: 23508769 Free PMC article.
-
The complete influenza hemagglutinin fusion domain adopts a tight helical hairpin arrangement at the lipid:water interface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11341-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006142107. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534508 Free PMC article.
-
Extending the applicability of P3D for structure determination of small molecules.Magn Reson (Gott). 2021 Apr 8;2(1):105-116. doi: 10.5194/mr-2-105-2021. eCollection 2021. Magn Reson (Gott). 2021. PMID: 37904779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prestegard J. H.; Al-Hashimi H. M.; Tolman J. R. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2000, 33, 371–424. - PubMed
-
- Bax A.; Kontaxis G.; Tjandra N. Meth. Enzym. 2001, 339, 127–174. - PubMed
-
- Ishii Y.; Markus M. A.; Tycko R. J. Biomol. NMR 2001, 21, 141–151. - PubMed
-
- Sass H. J.; Musco G.; Stahl S. J.; Wingfield P. T.; Grzesiek S. J. Biomol. NMR 2000, 18, 303–309. - PubMed
-
- Veglia G.; Opella S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11733–11734.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

