Introduction of cytochrome b mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a method that allows selection for both functional and non-functional cytochrome b proteins
- PMID: 18498758
- PMCID: PMC2601669
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.04.029
Introduction of cytochrome b mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a method that allows selection for both functional and non-functional cytochrome b proteins
Abstract
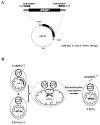
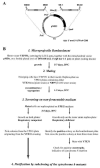
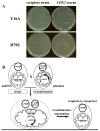
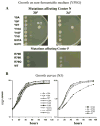
We have previously used inhibitors interacting with the Qn site of the yeast cytochrome bc(1) complex to obtain yeast strains with resistance-conferring mutations in cytochrome b as a means to investigate the effects of amino acid substitutions on Qn site enzymatic activity [M.G. Ding, J.-P. di Rago, B.L. Trumpower, Investigating the Qn site of the cytochrome bc1 complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with mutants resistant to ilicicolin H, a novel Qn site inhibitor, J. Biol. Chem. 281 (2006) 36036-36043.]. Although the screening produced various interesting cytochrome b mutations, it depends on the availability of inhibitors and can only reveal a very limited number of mutations. Furthermore, mutations leading to a respiratory deficient phenotype remain undetected. We therefore devised an approach where any type of mutation can be efficiently introduced in the cytochrome b gene. In this method ARG8, a gene that is normally encoded by nuclear DNA, replaces the naturally occurring mitochondrial cytochrome b gene, resulting in ARG8 expressed from the mitochondrial genome (ARG8(m)). Subsequently replacing ARG8(m) with mutated versions of cytochrome b results in arginine auxotrophy. Respiratory competent cytochrome b mutants can be selected directly by virtue of their ability to restore growth on non-fermentable substrates. If the mutated cytochrome b is non-functional, the presence of the COX2 respiratory gene marker on the mitochondrial transforming plasmid enables screening for cytochrome b mutants with a stringent respiratory deficiency (mit(-)). With this system, we created eight different yeast strains containing point mutations at three different codons in cytochrome b affecting center N. In addition, we created three point mutations affecting arginine 79 in center P. This is the first time mutations have been created for three of the loci presented here, and nine of the resulting mutants have never been described before.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chapter 27 An improved method for introducing point mutations into the mitochondrial cytochrome B gene to facilitate studying the role of cytochrome B in the formation of reactive oxygen species.Methods Enzymol. 2009;456:491-506. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)04427-3. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19348906
-
Investigating the Qn site of the cytochrome bc1 complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with mutants resistant to ilicicolin H, a novel Qn site inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 24;281(47):36036-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608026200. Epub 2006 Sep 20. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16987808
-
Combining Inhibitor Resistance-conferring Mutations in Cytochrome b Creates Conditional Synthetic Lethality in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8478-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809278200. Epub 2009 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19179332 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of the Multi-Subunit Cytochrome bc1 Complex in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 11;23(18):10537. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810537. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Respiratory complex III dysfunction in humans and the use of yeast as a model organism to study mitochondrial myopathy and associated diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov-Dec;1827(11-12):1346-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.11.015. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23220121 Review.
Cited by
-
The Cbp3-Cbp6 complex coordinates cytochrome b synthesis with bc(1) complex assembly in yeast mitochondria.J Cell Biol. 2012 Oct 1;199(1):137-50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201206040. Epub 2012 Sep 24. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23007649 Free PMC article.
-
Design of anti-parasitic and anti-fungal hydroxy-naphthoquinones that are less susceptible to drug resistance.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2011 May;177(1):12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21251932 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis of the cytochrome bc(1) complex and role of assembly factors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1817(2):276-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.11.009. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. Corrected and republished in: Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1817(6):872-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.03.003. PMID: 22138626 Free PMC article. Corrected and republished. Review.
-
A novel system to monitor mitochondrial translation in yeast.Microb Cell. 2018 Jan 13;5(3):158-164. doi: 10.15698/mic2018.03.621. Microb Cell. 2018. PMID: 29487862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding MG, di Rago J-P, Trumpower BL. Investigating the Qn site of the cytochrome bc1 complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with mutants resistant to ilicicolin H, a novel Qn site inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:36036–36043. - PubMed
-
- Bonnefoy N, Fox TD. Genetic transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Methods in Enzymology. 2001;350(5):97–111. - PubMed
-
- Dujon B. The Molecular Biology of the yeast Saccharomyces: Life Cycle and Inheritance. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 1981. p. 505.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

