Photodynamic treatment of endodontic polymicrobial infection in vitro
- PMID: 18498901
- PMCID: PMC2596687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.03.011
Photodynamic treatment of endodontic polymicrobial infection in vitro
Abstract
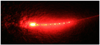
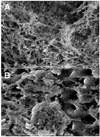
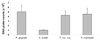
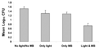
We investigated the photodynamic effects of methylene blue on multispecies root canal biofilms comprising Actinomyces israelii, Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies nucleatum, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Prevotella intermedia in experimentally infected root canals of extracted human teeth in vitro. The 4 test microorganisms were detected in root canals by using DNA probes. Scanning electron microscopy showed the presence of biofilms in root canals before therapy. Root canal systems were incubated with methylene blue (25 microg/mL) for 10 minutes followed by exposure to red light at 665 nm with an energy fluence of 30 J/cm(2). Light was delivered from a diode laser via a 250-microm diameter polymethyl methacrylate optical fiber that uniformly distributed light over 360 degrees. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) achieved up to 80% reduction of colony-forming unit counts. We concluded that PDT can be an effective adjunct to standard endodontic antimicrobial treatment when the PDT parameters are optimized.
Figures


References
-
- Sjögren U, Figdor D, Persson S, Sundqvist G. Influence of infection at the time of root filling on the outcome of endodontic treatment of teeth with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 1997;30:297–306. - PubMed
-
- Byström A, Sundqvist G. Bacteriologic evaluation of the effect of 0.5 percent sodium hypochlorite in endodontic therapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983;55:307–312. - PubMed
-
- Sundqvist G, Figdor D, Persson S, Sjögren U. Microbiologic analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1998;85:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Siqueira JF, Araújo MCP, Garcia PF, Fraga RC, Dantas CJS. Histological evaluation of the effectiveness of five instrumentation techniques for cleaning the apical third of root canals. J Endod. 1997;23:499–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

