Role of the interdomain linker in distance determination for remote cleavage by homing endonuclease I-TevI
- PMID: 18499124
- PMCID: PMC2699217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.047
Role of the interdomain linker in distance determination for remote cleavage by homing endonuclease I-TevI
Abstract
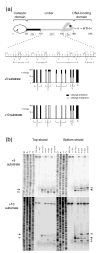
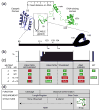
I-TevI is a modular intron-encoded endonuclease, consisting of an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal DNA-binding domain, joined by a 75 amino acid linker. This linker can be divided into three regions, starting at the N terminus: the deletion-intolerant (DI) region; the deletion-tolerant (DT) region; and a zinc finger, which acts as a distance determinant for cleavage. To further explore linker function, we generated deletion and substitution mutants that were tested for their preference to cleave at a particular distance or at the correct sequence. Our results demonstrate that the I-TevI linker is multi-functional, a property that sets it apart from junction sequences in most other proteins. First, the linker DI region has a role in I-TevI cleavage activity. Second, the DT linker region participates in distance determination, as evident from DT mutants that display a phenotype similar to that of the zinc-finger mutants in their selection of a cleavage site. Finally, NMR analysis of a freestanding 56 residue linker segment showed an unstructured stretch corresponding to the DI region and a portion of the DT region, followed by a beta-strand corresponding to the remainder of the DT region and containing a key distance-determining arginine, R129. Mutation of this arginine to alanine abolished distance determination and disrupted the beta-strand, indicating that the structure of the DT linker region has a role in cleavage at a fixed distance.
Figures





References
-
- Gokhale RS, Khosla C. Role of linkers in communication between protein modules. Cur Opin Chem Biol. 2000;4:22–27. - PubMed
-
- Wriggers W, Chakravarty S, Jennings PA. Control of protein functional dynamics by peptide linkers. Biopolymers. 2005;80:736–46. - PubMed
-
- Van Roey P, Derbyshire V. GIY-YIG homing endonucleases - beads on a string. In: Belfort M, Derbyshire V, Stoddard BL, Wood DW, editors. Homing Endonucleases and Inteins. Springer-Verlag; 2005. pp. 67–83.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

