Refractory idiopathic urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A injection
- PMID: 18499184
- PMCID: PMC2597793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.03.028
Refractory idiopathic urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A injection
Abstract
Purpose: We compared 200 U intradetrusor botulinum toxin A vs placebo in women with refractory idiopathic urge incontinence.
Materials and methods: This institutional review board approved, multicenter registered trial randomized women with refractory urge incontinence, detrusor overactivity incontinence and 6 or greater urge incontinence episodes in 3 days to botulinum toxin A or placebo at a 2:1 ratio. Refractory was defined as inadequate symptom control after 2 or more attempts at pharmacotherapy and 1 or more other first line therapies for detrusor overactivity incontinence. The primary outcome measure was time to failure, as evidenced by a Patient Global Impression of Improvement score of 4 or greater at least 2 months after injection, or changes in treatment (initiation or increase) at any time after injection. Safety data, including increased post-void residual volume, defined as more than 200 ml irrespective of symptoms, was obtained at specified time points.
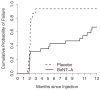
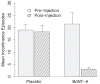
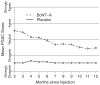
Results: Approximately 60% of the women who received botulinum toxin A had a clinical response based on the Patient Global Impression of Improvement. The median duration of their responses was 373 days, significantly longer than the 62 days or less for placebo (p <0.0001). In the botulinum toxin A group increased post-void residual urine (12 of 28 women or 43%) and urinary tract infection in those with increased post-void residual urine (9 of 12 or 75%) exceeded expected ranges. Further injections were stopped after 43 patients were randomized, including 28 to botulinum toxin A and 15 to placebo.
Conclusions: Local injection of 200 U botulinum toxin A was an effective and durable treatment for refractory overactive bladder. However, a transient post-void residual urine increase was experienced in 43% of patients. Botulinum toxin A for idiopathic overactive bladder is still under investigation.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00373789.
Figures
References
-
- Schurch B, Stohrer M, Kramer G, Schmid DM, Gaul G, Hauri D. Botulinum-A toxin for treating detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured patients: a new alternative to anticholinergic drugs? Preliminary results J Urol. 2000;164:692. - PubMed
-
- Giannantoni A, Di Stasi SM, Stephen RL, Bini V, Costantini E, Porena M. Intravesical resiniferatoxin versus botulinum-A toxin injections for neurogenic detrusor overactivity: a prospective randomized study. J Urol. 2004;172:240. - PubMed
-
- Karsenty G, Reitz A, Lindemann G, Boy S, Schurch B. Persistence of therapeutic effect after repeated injections of botulinum toxin type A to treat incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Urology. 2006;68:1193. - PubMed
-
- Kuo HC. Urodynamic evidence of effectiveness of botulinum A toxin injection in treatment of detrusor overactivity refractory to anticholinergic agents. Urology. 2004;63:868. - PubMed
-
- Sahai A, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Efficacy of botulinum toxin-A for treating idiopathic detrusor overactivity: results from a single center, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Urol. 2007;177:2231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HD041261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD041249/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054215/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10 HD54215/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 2U10 HD41250/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041248/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10 HD54136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 2U10 HD41267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054241/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041250/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10 HD54241/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 2U10 HD41261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 2U01 HD41249/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054214/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10 HD54214/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases