Orai, STIM1 and iPLA2beta: a view from a different perspective
- PMID: 18499724
- PMCID: PMC2538780
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.154997
Orai, STIM1 and iPLA2beta: a view from a different perspective
Abstract
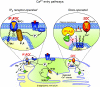
The mechanism of store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) remains one of the intriguing mysteries in the field of Ca(2+) signalling. Recent discoveries have resulted in the molecular identification of STIM1 as a Ca(2+) sensor in endoplasmic reticulum, Orai1 (CRACM1) as a plasma membrane channel that is activated by the store-operated pathway, and iPLA(2)beta as an essential component of signal transduction from the stores to the plasma membrane channels. Numerous studies have confirmed that molecular knock-down of any one of these three molecules impair SOCE in a wide variety of cell types, but their mutual relations are far from being understood. This report will focus on the functional roles of Orai1, STIM1 and iPLA(2)beta, and will address some specific questions about Orai1 and TRPC1, and their relation to SOC channels in excitable and non-excitable cells. Also, it will analyse the novel role of STIM1 as a trigger for CIF production, and the complex relationship between STIM1 and Orai1 expression, puncta formation and SOCE activation. It will highlight some of the most recent findings that may challenge simple conformational coupling models of SOCE, and will offer some new perspectives on the complex relationships between Orai1, STIM1 and iPLA(2)beta in the SOCE pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Ambudkar IS. TRPC1: a core component of store-operated calcium channels. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:96–100. - PubMed
-
- Balsinde J, Balboa MA. Cellular regulation and proposed biological functions of group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2 in activated cells. Cell Signal. 2005;17:1052–1062. - PubMed
-
- Balsinde J, Dennis EA. Function and inhibition of intracellular calcium-independent phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16069–16072. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

