JAK2, but not Src family kinases, is required for STAT, ERK, and Akt signaling in response to growth hormone in preadipocytes and hepatoma cells
- PMID: 18499741
- PMCID: PMC2505331
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0015
JAK2, but not Src family kinases, is required for STAT, ERK, and Akt signaling in response to growth hormone in preadipocytes and hepatoma cells
Abstract
Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), a tyrosine kinase that associates with the GH receptor and is activated by GH, has been implicated as a key mediator of GH signaling. Several published reports suggest that members of the Src family of tyrosine kinases may also participate in GH signaling. We therefore investigated the extent to which JAK2 and Src family kinases mediate GH activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) 1, 3, and 5a/b, ERKs 1 and 2, and Akt, in the highly GH-responsive cell lines 3T3-F442A preadipocytes and H4IIE hepatoma cells. GH activation of Src family kinases was not detected in either cell line. Further, blocking basal activity of Src kinases with the Src inhibitors PP1 and PP2 did not inhibit GH activation of STATs 1, 3, or 5a/b, or ERKs 1 and 2. When levels of JAK2 were depressed by short hairpin RNA in 3T3-F442A and H4IIE cells, GH-stimulated activation of STATs 1, 3, and 5a/b, ERKs 1 and 2, and Akt were significantly reduced; however, basal activity of Src family kinases was unaffected. These results were supported genetically by experiments showing that GH robustly activates JAK2, STATs 3 and 5a/b, ERKs 1 and 2, and Akt in murine embryonic fibroblasts derived from Src/Yes/ Fyn triple-knockout embryos that lack known Src kinases. These results strongly suggest that JAK2, but not Src family kinases, is critical for transducing these GH signals in 3T3-F442A and H4IIE cells.
Figures







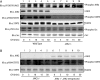
References
-
- Kaplan SL 1999 Hormonal regulation of growth and metabolic effects of growth hormone. In: Kostyo JL, ed. Handbook of physiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 129–143
-
- Scanes CG 1999 Hormones and growth in domestic animals. In: Kostyo JL, ed. Handbook of physiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 99–127
-
- Touw IP, De Koning JP, Ward AC, Hermans MH 2000 Signaling mechanisms of cytokine receptors and their perturbances in disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol 160:1–9 - PubMed
-
- Bartke A, Chandrashekar V, Turyn D, Steger RW, Debeljuk L, Winters TA, Mattison JA, Danilovich NA, Croson W, Wernsing DR, Kopchick JJ 1999 Effects of growth hormone overexpression and growth hormone resistance on neuroendocrine and reproductive functions in transgenic and knock-out mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 222:113–123 - PubMed
-
- Zhu T, Goh EL, Graichen R, Ling L, Lobie PE 2001 Signal transduction via the growth hormone receptor. Cell Signal 13:599–616 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

