Immunoparalysis and adverse outcomes from critical illness
- PMID: 18501759
- PMCID: PMC2474674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcl.2008.02.009
Immunoparalysis and adverse outcomes from critical illness
Abstract
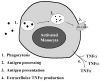
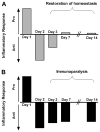
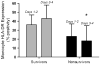
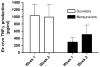
Proper immunologic balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory forces is necessary for recovery from critical illness. Persistence of a marked compensatory anti-inflammatory innate immune response after an insult is termed immunoparalysis. Critically ill patients demonstrating prolonged, severe reductions in monocyte HLA-DR expression or ex vivo tumor necrosis factor alpha production are at high risk for nosocomial infection and death. Reversal of immunoparalysis can be accomplished through the administration of immunostimulatory agents or tapering of exogenous immunosuppression. Evidence suggests that this may be associated with improved clinical outcomes. Immune-monitoring protocols are needed to identify patients who may benefit from immunomodulatory trials.
Figures
References
-
- Prophylactic intravenous administration of standard immune globulin as compared with core-lipopolysaccharide immune globulin in patients at high risk of postsurgical infection. The Intravenous Immunoglobulin Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 23;327(4):234–240. - PubMed
-
- Calandra T, Glauser MP, Schellekens J, Verhoef J. Treatment of gram-negative septic shock with human IgG antibody to Escherichia coli J5: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):312–319. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Fein AM, et al. A second large controlled clinical study of E5, a monoclonal antibody to endotoxin: results of a prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. The E5 Sepsis Study Group. Crit Care Med. 1995 Jun;23(6):994–1006. - PubMed
-
- Greenman RL, Schein RM, Martin MA, et al. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. Jama. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1097–1102. - PubMed
-
- McCloskey RV, Straube RC, Sanders C, Smith SM, Smith CR. Treatment of septic shock with human monoclonal antibody HA-1A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CHESS Trial Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Jul 1;121(1):1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

