Candida albicans ferric reductases are differentially regulated in response to distinct forms of iron limitation by the Rim101 and CBF transcription factors
- PMID: 18503007
- PMCID: PMC2446673
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00108-08
Candida albicans ferric reductases are differentially regulated in response to distinct forms of iron limitation by the Rim101 and CBF transcription factors
Abstract
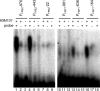
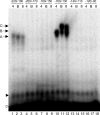
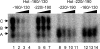
Iron is an essential nutrient that is severely limited in the mammalian host. Candida albicans encodes a family of 15 putative ferric reductases, which are required for iron acquisition and utilization. Despite the central role of ferric reductases in iron acquisition and mobilization, relatively little is known about the regulatory networks that govern ferric reductase gene expression in C. albicans. Here we have demonstrated the differential regulation of two ferric reductases, FRE2 and FRP1, in response to distinct iron-limited environments. FRE2 and FRP1 are both induced in alkaline-pH environments directly by the Rim101 transcription factor. However, FRP1 but not FRE2 is also induced by iron chelation. We have identified a CCAAT motif as the critical regulatory sequence for chelator-mediated induction and have found that the CCAAT binding factor (CBF) is essential for FRP1 expression in iron-limited environments. We found that a hap5Delta/hap5Delta mutant, which disrupts the core DNA binding activity of CBF, is unable to grow under iron-limited conditions. C. albicans encodes three CBF-dependent transcription factors, and we identified the Hap43 protein as the CBF-dependent transcription factor required for iron-limited responses. These studies provide key insights into the regulation of ferric reductase gene expression in the fungal pathogen C. albicans.
Figures


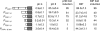
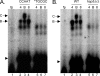
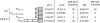


References
-
- Adams, A., D. E. Gotschling, C. A. Kaiser, and T. Stearns. 1997. Methods in yeast genetics, 1997 ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Barberis, A., G. Superti-Furga, and M. Busslinger. 1987. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell 50347-359. - PubMed
-
- Bensen, E. S., S. J. Martin, M. Li, J. Berman, and D. A. Davis. 2004. Transcriptional profiling in C. albicans reveals new adaptive responses to extracellular pH and functions for Rim101p. Mol. Microbiol. 541335-1351. - PubMed
-
- Blaiseau, P. L., E. Lesuisse, and J. M. Camadro. 2001. Aft2p, a novel iron-regulated transcription activator that modulates, with Aft1p, intracellular iron use and resistance to oxidative stress in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 27634221-34226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

