DTNBP1, a schizophrenia susceptibility gene, affects kinetics of transmitter release
- PMID: 18504299
- PMCID: PMC2396815
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200711021
DTNBP1, a schizophrenia susceptibility gene, affects kinetics of transmitter release
Abstract
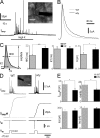
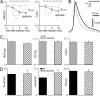
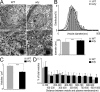
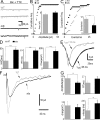
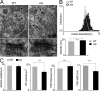
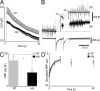
Schizophrenia is one of the most debilitating neuropsychiatric disorders, affecting 0.5-1.0% of the population worldwide. Its pathology, attributed to defects in synaptic transmission, remains elusive. The dystrobrevin-binding protein 1 (DTNBP1) gene, which encodes a coiled-coil protein, dysbindin, is a major susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. Our previous results have demonstrated that the sandy (sdy) mouse harbors a spontaneously occurring deletion in the DTNBP1 gene and expresses no dysbindin protein (Li, W., Q. Zhang, N. Oiso, E.K. Novak, R. Gautam, E.P. O'Brien, C.L. Tinsley, D.J. Blake, R.A. Spritz, N.G. Copeland, et al. 2003. Nat. Genet. 35:84-89). Here, using amperometry, whole-cell patch clamping, and electron microscopy techniques, we discovered specific defects in neurosecretion and vesicular morphology in neuroendocrine cells and hippocampal synapses at the single vesicle level in sdy mice. These defects include larger vesicle size, slower quantal vesicle release, lower release probability, and smaller total population of the readily releasable vesicle pool. These findings suggest that dysbindin functions to regulate exocytosis and vesicle biogenesis in endocrine cells and neurons. Our work also suggests a possible mechanism in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia at the synaptic level.
Figures

References
-
- Albillos, A., G. Dernick, H. Horstmann, W. Almers, G. Alvarez de Toledo, and M. Lindau. 1997. The exocytotic event in chromaffin cells revealed by patch amperometry. Nature. 389:509–512. - PubMed
-
- Artalejo, C.R., M.E. Adams, and A.P. Fox. 1994. Three types of Ca2+ channel trigger secretion with different efficacies in chromaffin cells. Nature. 367:72–76. - PubMed
-
- Barbara, J.G., J.C. Poncer, R.A. McKinney, and K. Takeda. 1998. An adrenal slice preparation for the study of chromaffin cells and their cholinergic innervation. J. Neurosci. Methods. 80:181–189. - PubMed
-
- Benson, M.A., S.E. Newey, E. Martin-Rendon, R. Hawkes, and D.J. Blake. 2001. Dysbindin, a novel coiled-coil-containing protein that interacts with the dystrobrevins in muscle and brain. J. Biol. Chem. 276:24232–24241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

