Tissue transglutaminase modulates alpha-synuclein oligomerization
- PMID: 18505736
- PMCID: PMC2492824
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.036103.108
Tissue transglutaminase modulates alpha-synuclein oligomerization
Abstract
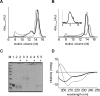
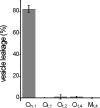
We have studied the interaction of the enzyme tissue transglutaminase (tTG), catalyzing cross-link formation between protein-bound glutamine residues and primary amines, with Parkinson's disease-associated alpha-synuclein protein variants at physiologically relevant concentrations. We have, for the first time, determined binding affinities of tTG for wild-type and mutant alpha-synucleins using surface plasmon resonance approaches, revealing high-affinity nanomolar equilibrium dissociation constants. Nanomolar tTG concentrations were sufficient for complete inhibition of fibrillization by effective alpha-synuclein cross-linking, resulting predominantly in intramolecularly cross-linked monomers accompanied by an oligomeric fraction. Since oligomeric species have a pathophysiological relevance we further investigated the properties of the tTG/alpha-synuclein oligomers. Atomic force microscopy revealed morphologically similar structures for oligomers from all alpha-synuclein variants; the extent of oligomer formation was found to correlate with tTG concentration. Unlike normal alpha-synuclein oligomers the resultant structures were extremely stable and resistant to GdnHCl and SDS. In contrast to normal beta-sheet-containing oligomers, the tTG/alpha-synuclein oligomers appear to be unstructured and are unable to disrupt phospholipid vesicles. These data suggest that tTG binds equally effective to wild-type and disease mutant alpha-synuclein variants. We propose that tTG cross-linking imposes structural constraints on alpha-synuclein, preventing the assembly of structured oligomers required for disruption of membranes and for progression into fibrils. In general, cross-linking of amyloid forming proteins by tTG may prevent the progression into pathogenic species.
Figures


References
-
- Andringa, G., Lam, K.Y., Chegary, M., Wang, X., Chase, T.N., Bennett, M.C. Tissue transglutaminase catalyzes the formation of α-synuclein crosslinks in Parkinson's disease. FASEB J. 2004;18:932–934. - PubMed
-
- Bendit, E.G., Ross, D. A technique for obtaining the ultraviolet absorption spectrum of solid keratin. Appl. Spectros. 1961;15:103–105.
-
- Chen, P.S., Toribara, T.Y., Warner, H. Microdetermination of phosphorus. Anal. Chem. 1956;28:1756–1758.
-
- Eliezer, D., Kutluay, E., Bussell R., Jr, Browne, G. Conformational properties of α-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;307:1061–1073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

