Dose-effect study of domperidone as a galactagogue in preterm mothers with insufficient milk supply, and its transfer into milk
- PMID: 18507654
- PMCID: PMC2492930
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03207.x
Dose-effect study of domperidone as a galactagogue in preterm mothers with insufficient milk supply, and its transfer into milk
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the possibility of a dose-response relationship for the use of domperidone in treating insufficient milk supply in mothers of preterm infants, and to quantify the exposure of the breastfed infant to domperidone.
Methods: Six preterm mothers received domperidone (30 mg daily or 60 mg daily) in a double-blind, randomized, crossover trial. Milk production and serum prolactin were measured before and during the trial, and domperidone concentration in milk was measured during drug treatment.
Results: For milk production, two of the mothers were 'nonresponders', whereas the other four were 'responders' and showed a significant increase in milk production from 8.7 +/- 3.1 g h(-1) in the run-in phase (mean +/- SEM), 23.6 +/- 3.9 g h(-1) for the 30-mg dose (P = 0.0217) and 29.4 +/- 6.6 g h(-1) for the 60-mg dose (P = 0.0047). In all participants, serum prolactin was significantly increased for both doses, but the response was not dose dependent. Median (interquartile range) domperidone concentrations in milk over a dose interval at steady-state were 0.28 microg l(-1) (0.24-0.43) and 0.49 microg l(-1) (0.33-0.72) for the 30-mg and 60-mg doses, respectively. The mean relative infant dose was 0.012% at 30 mg daily and 0.009% at 60 mg daily.
Conclusion: In one-third of mothers, domperidone did not increase milk production. In the remainder, milk production increased at both domperidone doses, and there was a trend for a dose-response relationship. The amount of domperidone that transfers into milk was extremely low, and infant exposure via breastfeeding was not considered to be significant.
Figures
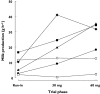
 ); PG, (▪)
); PG, (▪)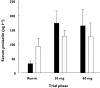

References
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Policy statement. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2005;115:496–506.
-
- Dewey KG, Heinig MJ, Nommsen-Rivers LA. Differences in morbidity between breast-fed and formula-fed infants. J Pediatr. 1995;126:696–702. - PubMed
-
- Uauy RD, Birch DG, Birch EE, Tyson JE, Hoffman DR. Effect of dietary omega-3 fatty acids on retinal function of very-low-birth-weight neonates. Pediatr Res. 1990;28:485–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

