The ability of atropine to prevent and reverse the negative chronotropic effect of fingolimod in healthy subjects
- PMID: 18507656
- PMCID: PMC2492924
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03199.x
The ability of atropine to prevent and reverse the negative chronotropic effect of fingolimod in healthy subjects
Abstract
Aims: The authors determined whether intravenous atropine can prevent or counteract the negative chronotropic effect of the immunomodulator fingolimod.
Methods: In this randomized, placebo-controlled, two-period, crossover study, 12 healthy subjects received 5 mg fingolimod orally concurrently with intravenous atropine (titrated to a heart rate of 110-120 beats min(-1)) or intravenous placebo. A second group of 12 subjects received atropine/placebo 4 h after the fingolimod dose. Continuous telemetry measurements were made for 24 h after each fingolimod dose.
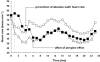
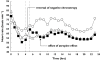
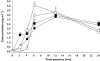
Results: Fingolimod administration alone yielded a heart rate nadir of 51 +/- 5 beats min(-1) at a median 4 h postdose with heart rate remaining depressed at 51-64 beats min(-1) over the rest of the day. Concurrent administration of fingolimod and atropine yielded a nadir of 66 +/- 6 beats min(-1) resulting in an atropine: placebo ratio (90% confidence interval) of 1.30 (1.22, 1.36). When atropine was administered at the time of the nadir, it was able to reverse the negative chronotropic effect of fingolimod from a heart rate of 56 +/- 9 beats min(-1) (placebo) to 64 +/- 8 beats min(-1) (atropine) resulting in an atropine: placebo ratio of 1.15 (1.04, 1.26). Atropine had no influence on the pharmacokinetics of fingolimod.
Conclusions: Atropine administered concurrently with fingolimod prevented the heart rate nadir that typically occurs 4 h postdose. Atropine administered at the time of the heart rate nadir was able to reverse the negative chronotropic effect of fingolimod.
Figures
References
-
- Kappos L, Antel J, Comi G. Oral fingolimod (fty720) for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1124–40. - PubMed
-
- Massberg S, von Andrian UH. Fingolimod and sphingosine-1-phosphate: modifiers of lymphocyte migration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1088–91. - PubMed
-
- Hla T. Signaling and biological actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Pharmacol Res. 2003;47:401–7. - PubMed
-
- Schmouder RL, Barilla D, Wang Y. FTY720: placebo-controlled study of the effect on cardiac rate and rhythm in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;46:895–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

