Porous silicon in drug delivery devices and materials
- PMID: 18508154
- PMCID: PMC2710886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.03.017
Porous silicon in drug delivery devices and materials
Abstract
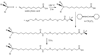
Porous Si exhibits a number of properties that make it an attractive material for controlled drug delivery applications: The electrochemical synthesis allows construction of tailored pore sizes and volumes that are controllable from the scale of microns to nanometers; a number of convenient chemistries exist for the modification of porous Si surfaces that can be used to control the amount, identity, and in vivo release rate of drug payloads and the resorption rate of the porous host matrix; the material can be used as a template for organic and biopolymers, to prepare composites with a designed nanostructure; and finally, the optical properties of photonic structures prepared from this material provide a self-reporting feature that can be monitored in vivo. This paper reviews the preparation, chemistry, and properties of electrochemically prepared porous Si or SiO2 hosts relevant to drug delivery applications.
Figures


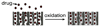
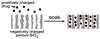

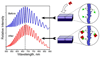

References
-
- Collins RT, Fauchet PM, Tischler MA. Porous silicon: from luminescence to LEDs. Phys. Today. 1997;50:24–31.
-
- Lazarouk S, Jaguiro P, Katsouba S, et al. Stable electroluminescence from reverse biased n-type porous silicon-aluminum Schottky junction device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996;68:2108–2110.
-
- Steiner P, Kozlowski F, Lang W. Light-emitting porous silicon diode with an increased electroluminescence quantum efficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993;62:2700–2702.
-
- Richter A, Steiner P, Kozlowski F, Lang W. Current-induced light emission from a porous Si device. IEEE Elec. Dev. Lett. 1991;12:691–692.
-
- Foucaran A, Pascal-Delannoy F, Giani A, Sackda A, Combette P, Boyer A. Porous silicon layers used for gas sensor applications. Thin Solid Films. 1997;297:317–320.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

