Sensory roles of neuronal cilia: cilia development, morphogenesis, and function in C. elegans
- PMID: 18508635
- PMCID: PMC3124812
- DOI: 10.2741/3129
Sensory roles of neuronal cilia: cilia development, morphogenesis, and function in C. elegans
Abstract
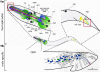
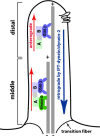
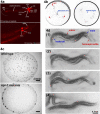
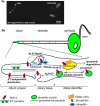
In the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, cilia are found on the dendritic endings of sensory neurons. C. elegans cilia are classified as 'primary' or 'sensory' according to the '9+0' axonemal ultrastructure (nine doublet outer microtubules with no central microtubule pair) and lack of motility, characteristics of '9+2' cilia. The C. elegans ciliated nervous system allows the animal to perceive environmental stimuli and make appropriate developmental, physiological, and behavioral decisions. In vertebrates, the biological significance of primary cilia had been largely neglected. Recent findings have placed primary/sensory cilia in the center of cellular signaling and developmental processes. Studies using genetic model organisms such as C. elegans identified the link between ciliary dysfunction and human ciliopathies. Future studies in the worm will address important basic questions regarding ciliary development, morphogenesis, specialization, and signaling functions.
Figures

References
-
- Ward S, Thomson N, White JG, Brenner S. Electron microscopical reconstruction of the anterior sensory anatomy of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Comp Neurol. 1975;160:313–37. - PubMed
-
- Ware RW, Clark DV, Crossland K, Russell RL. The nerve ring of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: Sensory input and motor output. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975;162:71–110.
-
- White JG, Southgate E, Thomson JN, Brenner S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: the mind of a worm. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1986;314:1–340. - PubMed
-
- Perkins LA, Hedgecock EM, Thomson JN, Culotti JG. Mutant sensory cilia in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1986;117:456–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
