Tonically active inhibition selectively controls feedforward circuits in mouse barrel cortex
- PMID: 18509076
- PMCID: PMC2525715
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01360.2007
Tonically active inhibition selectively controls feedforward circuits in mouse barrel cortex
Abstract
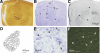
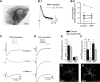
Tonic inhibition mediated by extrasynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA A) receptors is a powerful conductance that controls cell excitability. Throughout the CNS, tonic inhibition is expressed at varying degrees across different cell types. Despite a rich history of cortical interneuron diversity, little is known about tonic inhibition in the different classes of cells in the cerebral cortex. We therefore examined the cell-type specificity and functional significance of tonic inhibition in layer 4 of the mouse somatosensory barrel cortex. In situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry showed moderate delta-subunit expression across the barrel structures. Whole cell patch-clamp recordings additionally indicated that significant levels of tonic inhibition can be found across cell types, with differences in the magnitude of inhibition between cell types. To activate tonic currents, we used 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol (THIP, a superagonist at delta-subunit-containing GABA A receptors) at a concentration that did not affect synaptic decay kinetics. THIP produced greater shifts in baseline holding current in inhibitory cells (low-threshold spiking [LTS], 109 +/- 17 pA; fast spiking [FS], 111 +/- 15 pA) than in excitatory cells (39 +/- 10 pA; P < 0.001). In addition to these differences across cell types, there was also variability within inhibitory cells. FS cells with faster action potentials had larger baseline shifts. Because FS cells are known mediators of feedforward inhibition, we tested whether THIP-induced tonic conductance selectively controls feedforward circuits. THIP application resulted in the abolishment of the inhibitory postsynaptic potential in thalamic-evoked disynaptic responses in a subset of excitatory neurons. These data suggest multiple feedforward circuits can be differentiated by the inhibitory control of the presynaptic inhibitory neuron.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Long-term sensory deprivation selectively rearranges functional inhibitory circuits in mouse barrel cortex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 21;106(29):12156-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900922106. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19584253 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of thalamic excitability by 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[4,5-c]pyridine-3-ol: a selective role for delta-GABA(A) receptors.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Mar;29(6):1177-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06680.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19302153 Free PMC article.
-
An extrasynaptic GABAA receptor mediates tonic inhibition in thalamic VB neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Dec;94(6):4491-501. doi: 10.1152/jn.00421.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 14. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 16162835
-
Function and modulation of delta-containing GABA(A) receptors.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009 Dec;34 Suppl 1:S67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.08.010. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19766404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition on neuronal excitability varies across brain region and cell type.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Feb 3;8:3. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00003. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 24550784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Seizure-induced alterations in fast-spiking basket cell GABA currents modulate frequency and coherence of gamma oscillation in network simulations.Chaos. 2013 Dec;23(4):046109. doi: 10.1063/1.4830138. Chaos. 2013. PMID: 24387588 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal study of hemodynamics and dendritic membrane potential changes in the mouse cortex following a soft cranial window installation.Neurophotonics. 2019 Jan;6(1):015006. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.6.1.015006. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Neurophotonics. 2019. PMID: 30820438 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term sensory deprivation selectively rearranges functional inhibitory circuits in mouse barrel cortex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 21;106(29):12156-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900922106. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19584253 Free PMC article.
-
The 4-aminopyridine in vitro epilepsy model analyzed with a perforated multi-electrode array.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Jun;60(7-8):1142-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.10.007. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 20955719 Free PMC article.
-
Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors: form, pharmacology, and function.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 14;29(41):12757-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3340-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19828786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agmon A, Connors BW. Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience 41: 365–379, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, Braestrup C, Bateson AN, Langer SZ. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev 50: 291–313, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

