Accuracy of model-based RSA contour reduction in a typical clinical application
- PMID: 18509712
- PMCID: PMC2584241
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0287-3
Accuracy of model-based RSA contour reduction in a typical clinical application
Abstract
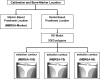
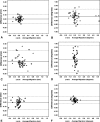
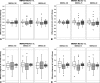
Marker-based roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis (RSA) is an accurate method for measuring in vivo implant migration, which requires attachment of tantalum markers to the implant. Model-based RSA allows migration measurement without implant markers; digital pose estimation, which can be thought of as casting a shadow of a surface model of the implant into the stereoradiographs, is used instead. The number of surface models required in a given clinical study depends on the number of implanted sizes and design variations of prostheses. Contour selection can be used to limit pose estimation to areas of the prosthesis that do not vary with design, reducing the number of surface models required. The effect of contour reduction on the accuracy of the model-based method was investigated using three different contour selection schemes on tibial components in 24 patients at 3 and 6 month followup. The agreement interval (mean +/- 2 standard deviations), which bounds the differences between the marker-based and model-based methods with contour reduction was smaller than -0.028 +/- 0.254 mm. The data suggest that contour reduction does not result in unacceptable loss of model-based RSA accuracy, and that the model-based method can be used interchangeably with the marker-based method for measuring tibial component migration.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

