The microRNA miR-1 regulates a MEF-2-dependent retrograde signal at neuromuscular junctions
- PMID: 18510933
- PMCID: PMC2553566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.035
The microRNA miR-1 regulates a MEF-2-dependent retrograde signal at neuromuscular junctions
Abstract
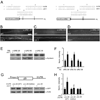
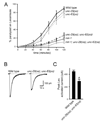
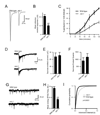
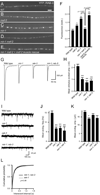
We show that miR-1, a conserved muscle-specific microRNA, regulates aspects of both pre- and postsynaptic function at C. elegans neuromuscular junctions. miR-1 regulates the expression level of two nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunits (UNC-29 and UNC-63), thereby altering muscle sensitivity to acetylcholine (ACh). miR-1 also regulates the muscle transcription factor MEF-2, which results in altered presynaptic ACh secretion, suggesting that MEF-2 activity in muscles controls a retrograde signal. The effect of the MEF-2-dependent retrograde signal on secretion is mediated by the synaptic vesicle protein RAB-3. Finally, acute activation of levamisole-sensitive nAChRs stimulates MEF-2-dependent transcriptional responses and induces the MEF-2-dependent retrograde signal. We propose that miR-1 refines synaptic function by coupling changes in muscle activity to changes in presynaptic function.
Figures


References
-
- Brown LA, Jones AK, Buckingham SD, Mee CJ, Sattelle DB. Contributions from Caenorhabditis elegans functional genetics to antiparasitic drug target identification and validation: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, a case study. Int J Parasitol. 2006;36:617–624. - PubMed
-
- Cao X, Yeo G, Muotri AR, Kuwabara T, Gage FH. NONCODING RNAS IN THE MAMMALIAN CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 2006;29:77–103. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Krause M, Draper B, Weintraub H, Fire A. Body-wall muscle formation in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos that lack the MyoD homolog hlh-1. Science. 1992;256:240–243. - PubMed
-
- Davis GW, Bezprozvanny I. MAINTAINING THE STABILITY OF NEURAL FUNCTION: A Homeostatic Hypothesis. Annual Review of Physiology. 2001;63:847–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

