Pre-folding IkappaBalpha alters control of NF-kappaB signaling
- PMID: 18511071
- PMCID: PMC2519148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.02.053
Pre-folding IkappaBalpha alters control of NF-kappaB signaling
Abstract
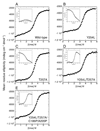
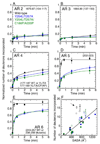
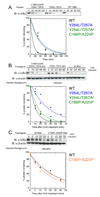
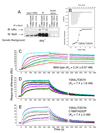
Transcription complex components frequently show coupled folding and binding but the functional significance of this mode of molecular recognition is unclear. IkappaBalpha binds to and inhibits the transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB via its ankyrin repeat (AR) domain. The beta-hairpins in ARs 5-6 in IkappaBalpha are weakly-folded in the free protein, and their folding is coupled to NF-kappaB binding. Here, we show that introduction of two stabilizing mutations in IkappaBalpha AR 6 causes ARs 5-6 to fold cooperatively to a conformation similar to that in NF-kappaB-bound IkappaBalpha. Free IkappaBalpha is degraded by a proteasome-dependent but ubiquitin-independent mechanism, and this process is slower for the pre-folded mutants both in vitro and in cells. Interestingly, the pre-folded mutants bind NF-kappaB more weakly, as shown by both surface plasmon resonance and isothermal titration calorimetry in vitro and immunoprecipitation experiments from cells. One consequence of the weaker binding is that resting cells containing these mutants show incomplete inhibition of NF-kappaB activation; they have significant amounts of nuclear NF-kappaB. Additionally, the weaker binding combined with the slower rate of degradation of the free protein results in reduced levels of nuclear NF-kappaB upon stimulation. These data demonstrate clearly that the coupled folding and binding of IkappaBalpha is critical for its precise control of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regions of IkappaBalpha that are critical for its inhibition of NF-kappaB.DNA interaction fold upon binding to NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 12;103(50):18951-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605794103. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17148610 Free PMC article.
-
The IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex has two hot spots, one at either end of the interface.Protein Sci. 2008 Dec;17(12):2051-8. doi: 10.1110/ps.037481.108. Epub 2008 Sep 29. Protein Sci. 2008. PMID: 18824506 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of a ternary complex of NF-kappaB and IkappaBalpha with DNA provides insights into how IkappaBalpha removes NF-kappaB from transcription sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1367-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014323108. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21220295 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of system control of NF-kappaB signaling by IkappaBalpha.Biochemistry. 2010 Mar 2;49(8):1560-7. doi: 10.1021/bi901948j. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20055496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of IkappaBalpha function and NF-kappaB signaling: AEBP1 is a novel proinflammatory mediator in macrophages.Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:823821. doi: 10.1155/2010/823821. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. PMID: 20396415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the bipartite degron that regulates ubiquitin-independent degradation of thymidylate synthase.Biosci Rep. 2013 Jan 18;33(1):165-73. doi: 10.1042/BSR20120112. Biosci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23181752 Free PMC article.
-
Complex energy landscape of a giant repeat protein.Structure. 2013 Nov 5;21(11):1954-65. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.08.028. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Structure. 2013. PMID: 24120762 Free PMC article.
-
DNA and IκBα Both Induce Long-Range Conformational Changes in NFκB.J Mol Biol. 2017 Apr 7;429(7):999-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.02.017. Epub 2017 Feb 27. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28249778 Free PMC article.
-
ANKRD54 preferentially selects Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) from a Human Src-Homology 3 (SH3) domain library.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 3;12(4):e0174909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174909. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28369144 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule FRET reveals the native-state dynamics of the IκBα ankyrin repeat domain.J Mol Biol. 2013 Jul 24;425(14):2578-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.04.015. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23619335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Takada Y, Boriek AM, Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB: its role in health and disease. J. Mol. Med. 2004;82:434–448. - PubMed
-
- Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2723–2735. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988;242:540–546. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS., Jr The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

