Killing of human melanoma cells induced by activation of class I interferon-regulated signaling pathways via MDA-7/IL-24
- PMID: 18511292
- PMCID: PMC2582834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.04.010
Killing of human melanoma cells induced by activation of class I interferon-regulated signaling pathways via MDA-7/IL-24
Abstract
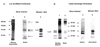
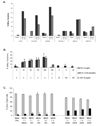
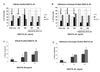
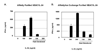
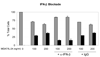
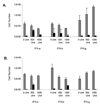
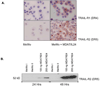
Restoration of the tumor-suppression function by gene transfer of the melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7 (MDA7)/interleukin 24 (IL-24) successfully induces apoptosis in melanoma tumors in vivo. To address the molecular mechanisms involved, we previously revealed that MDA7/IL-24 treatment of melanoma cells down-regulates interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-1 expression and concomitantly up-regulates IRF-2 expression, which competes with the activity of IRF-1 and reverses the induction of IRF-1-regulated inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Interferons (IFNs) influence melanoma cell survival by modulating apoptosis. A class I IFN (IFN-alpha) has been approved for the treatment of advanced melanoma with some limited success. A class II IFN (IFN-gamma), on the other hand, supports melanoma cell survival, possibly through constitutive activation of iNOS expression. We therefore conducted this study to explore the molecular pathways of MDA7/IL-24 regulation of apoptosis via the intracellular induction of IFNs in melanoma. We hypothesized that the restoration of the MDA7/IL-24 axis leads to upregulation of class I IFNs and induction of the apoptotic cascade. We found that MDA7/IL-24 induces the secretion of endogenous IFN-beta, another class I IFN, leading to the arrest of melanoma cell growth and apoptosis. We also identified a series of apoptotic markers that play a role in this pathway, including the regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and Fas-FasL. In summary, we described a novel pathway of MDA7/IL-24 regulation of apoptosis in melanoma tumors via endogenous IFN-beta induction followed by IRF regulation and TRAIL/FasL system activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preferential induction of apoptosis by interferon (IFN)-beta compared with IFN-alpha2: correlation with TRAIL/Apo2L induction in melanoma cell lines.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Jun;7(6):1821-31. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11410525
-
Activation of the Fas-FasL signaling pathway by MDA-7/IL-24 kills human ovarian cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 15;65(8):3017-24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3758. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15833826
-
IRF-1 inhibits NF-κB activity, suppresses TRAF2 and cIAP1 and induces breast cancer cell specific growth inhibition.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(7):1029-41. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1046646. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26011589 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB augments antitumor activity of adenovirus-mediated melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 against lung cancer cells via mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 activation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Apr;6(4):1440-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0374. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17431123
-
Augmentation of effects of interferon-stimulated genes by reversal of epigenetic silencing: potential application to melanoma.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007 Oct-Dec;18(5-6):491-501. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.06.022. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007. PMID: 17689283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Theranostic Tripartite Cancer Terminator Virus for Cancer Therapy and Imaging.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;13(4):857. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040857. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670594 Free PMC article.
-
Sublytic C5b-9 complexes induce apoptosis of glomerular mesangial cells in rats with Thy-1 nephritis through role of interferon regulatory factor-1-dependent caspase 8 activation.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16410-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.319566. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22427665 Free PMC article.
-
A new oncolytic adenoviral vector carrying dual tumour suppressor genes shows potent anti-tumour effect.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Jun;16(6):1298-309. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01396.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21794078 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer terminator viruses (CTV): A better solution for viral-based therapy of cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Aug;233(8):5684-5695. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26421. Epub 2018 Feb 27. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29278667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhinovirus-induced modulation of gene expression in bronchial epithelial cells from subjects with asthma.Mucosal Immunol. 2010 Jan;3(1):69-80. doi: 10.1038/mi.2009.109. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Mucosal Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19710636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madireddi MT, Su ZZ, Young CS, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Mda-7, a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene with promise for cancer gene therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;465:239–261. - PubMed
-
- Mhashilkar AM, Schrock RD, Hindi M, Liao J, Sieger K, Kourouma F, Zou-Yang XH, Onishi E, Takh O, Vedvick TS, Fanger G, Stewart L, Watson GJ, Snary D, Fisher PB, Saeki T, Roth JA, Ramesh R, Chada S. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7 (mda-7): a novel anti-tumor gene for cancer gene therapy. Mol Med. 2001;7:271–282. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Valerie K, Dent P, Fisher PB. mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:10054–10059. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramesh R, Mhashilkar AM, Tanaka F, Saito Y, Branch CD, Sieger K, Mumm JB, Stewart AL, Boquoi A, Dumoutier L, Grimm EA, Renauld JC, Kotenko S, Chada S. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7/ interleukin (IL)-24 is a novel ligand that regulates angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5105–5113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

