High insulinlike growth factor binding protein 1 level predicts incident congestive heart failure in the elderly
- PMID: 18513511
- PMCID: PMC3286655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2007.12.031
High insulinlike growth factor binding protein 1 level predicts incident congestive heart failure in the elderly
Abstract
Background: Low levels of insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-I) may influence the development of age-related cardiovascular diseases including congestive heart failure (CHF). Insulinlike growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1), which increases during catabolic states and inhibits anabolic IGF-I effects, is increased in patients with CHF and has been associated prospectively with increased mortality among older adults and survivors of myocardial infarction. We investigated the association between fasting plasma levels of IGF-I, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-3, and insulin and risk of incident CHF in the prospective Cardiovascular Health Study.
Methods: From among 5,888 adults 65 years old and older in the Cardiovascular Health Study, we studied 566 incident CHF cases and 1,072 comparison subjects after exclusion of underweight individuals (body mass index <18.5 kg/m(2)) and insulin users. Hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs for CHF were estimated after adjustment for age, race, sex, hypertension, systolic blood pressure, lipid levels, left ventricular hypertrophy, coronary disease, C-reactive protein, health status, diabetes, and body mass index.
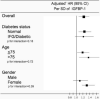
Results: High baseline IGFBP-1 level was a significant predictor of CHF, independent of established CHF risk factors and inflammation markers. The HR per SD of IGFBP-1 was 1.22 (95% CI 1.07-1.39, P < .01). Relative to the lowest IGFBP-1 tertile, the HR was 1.29 (95% CI 0.96-1.74, P = .09) for the second IGFBP-1 tertile and 1.47 (95% CI 1.06-2.04; P = .02) for the highest IGFBP-1 tertile (tertile cut points 19.5 and 35.8 ng/mL). Total IGF-I, IGFBP-3, or insulin levels had no association with CHF after adjustment for CHF risk factors.
Conclusions: High circulating IGFBP-1 level may be a CHF risk factor among older adults.
Figures
References
-
- Holzenberger M, Hamard G, Zaoui R, et al. Experimental IGF-I receptor deficiency generates a sexually dimorphic pattern of organ-specific growth deficits in mice, affecting fat tissue in particular. Endocrinology. 2001;142(10):4469–78. - PubMed
-
- Longo VD, Finch CE. Evolutionary medicine: from dwarf model systems to healthy centenarians? Science. 2003;299(5611):1342–6. - PubMed
-
- Holzenberger M, Dupont J, Ducos B, et al. IGF-1 receptor regulates lifespan and resistance to oxidative stress in mice. Nature. 2003;421(6919):182–7. - PubMed
-
- Gotz W, Kunert D, Zhang D, et al. Insulin-like growth factor system components in the periodontium during tooth root resorption and early repair processes in the rat. Eur J Oral Sci. 2006;114(4):318–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01HL083760-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075516/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC015103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031890/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

