Structures and functional implications of an AMP-binding cystathionine beta-synthase domain protein from a hyperthermophilic archaeon
- PMID: 18513746
- PMCID: PMC2577872
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.073
Structures and functional implications of an AMP-binding cystathionine beta-synthase domain protein from a hyperthermophilic archaeon
Abstract
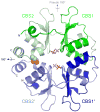
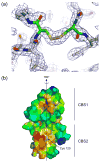
Cystathionine beta-synthase domains are found in a myriad of proteins from organisms across the tree of life and have been hypothesized to function as regulatory modules that sense the energy charge of cells. Here we characterize the structure and stability of PAE2072, a dimeric tandem cystathionine beta-synthase domain protein from the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum. Crystal structures of the protein in unliganded and AMP-bound forms, determined at resolutions of 2.10 and 2.35 A, respectively, reveal remarkable conservation of key functional features seen in the gamma subunit of the eukaryotic AMP-activated protein kinase. The structures also confirm the presence of a suspected intermolecular disulfide bond between the two subunits that is shown to stabilize the protein. Our AMP-bound structure represents a first step in investigating the function of a large class of uncharacterized prokaryotic proteins. In addition, this work extends previous studies that have suggested that, in certain thermophilic microbes, disulfide bonds play a key role in stabilizing intracellular proteins and protein-protein complexes.
Figures
References
-
- Gilbert HF. Molecular and cellular aspects of thiol-disulfide exchange. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:69–172. - PubMed
-
- Prinz WA, Aslund F, Holmgren A, Beckwith J. The role of the thioredoxin and glutaredoxin pathways in reducing protein disulfide bonds in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:15661–7. - PubMed
-
- Kadokura H, Katzen F, Beckwith J. Protein disulfide bond formation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:111–35. - PubMed
-
- Chiu HJ, Johnson E, Schroder I, Rees DC. Crystal structures of a novel ferric reductase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus and its complex with NADP+ Structure. 2001;9:311–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

