Antinociception occurs with a reversal in alpha 2-adrenoceptor regulation of TNF production by peripheral monocytes/macrophages from pro- to anti-inflammatory
- PMID: 18514187
- PMCID: PMC2587399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.04.043
Antinociception occurs with a reversal in alpha 2-adrenoceptor regulation of TNF production by peripheral monocytes/macrophages from pro- to anti-inflammatory
Abstract
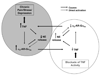
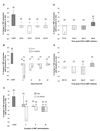
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) plays a role in neuropathic pain. During neuropathic pain development in the chronic constriction injury model, elevated TNF levels in the brain occur in association with enhanced alpha 2-adrenoceptor inhibition of norepinephrine release. alpha 2-Adrenoceptors are also located on peripheral macrophage where they normally function as pro-inflammatory, since they increase the production of the cytokine TNF, a proximal mediator of inflammation. How the central increase in TNF affects peripheral alpha 2-adrenoceptor function was investigated. Male, Sprague-Dawley rats had four loose ligatures placed around the right sciatic nerve. Thermal hyperalgesia was determined by comparing hind paw withdrawal latencies between chronic constriction injury and sham-operated rats. Chronic constriction injury increased TNF immunoreactivity at the lesion and the hippocampus. Amitriptyline, an antidepressant that is used as an analgesic, was intraperitoneally administered (10 mg/kg) starting simultaneous with ligature placement (day-0) or at days-4 or -6 post-surgery. Amitriptyline treatment initiated at day-0 or day-4 post-ligature placement alleviated hyperalgesia. When initiated at day-0, amitriptyline prevented increased TNF immunoreactivity in the hippocampus and at the lesion. A peripheral inflammatory response, macrophage production of TNF, was also assessed in the current study. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated production of TNF by whole blood cells and peritoneal macrophages was determined following activation of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor in vitro. alpha 2-Adrenoceptor regulation of TNF production from peripheral immune-effector cells reversed from potentiation in controls to inhibition in chronic constriction injured rats. This effect is accelerated with amitriptyline treatment initiated at day-0 or day-4 post-ligature placement. Amitriptyline treatment initiated day-6 post-ligature placement did not alleviate hyperalgesia and prevented the switch from potentiation to inhibition in alpha 2-adrenoceptor regulation of TNF production. Recombinant rat TNF i.c.v. microinfusion reproduces the response of peripheral macrophages from rats with chronic constriction injury. A reversal in peripheral alpha 2-adrenoceptor regulation of TNF production from pro- to anti-inflammatory is associated with effective alleviation of thermal hyperalgesia. Thus, alpha 2-adrenoceptor regulation of peripheral TNF production may serve as a potential biomarker to evaluate therapeutic regimens.
Figures










References
-
- Ardid D, Jourdan D, Mestre C, Villanueva L, Le Bars D, Eschalier A. Involvement of bulbospinal pathways in the antinociceptive effect of clomipramine in the rat. Brain Res. 1995;695:253–256. - PubMed
-
- Attal N, Bouhassira D. Mechanisms of pain in peripheral neuropathy. Acta. Neurologica Scandinavica. Supplementum. 1999;173:12–24. discussion 48–52. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Moinuddin A, Morley JE. Regional transport of TNF-alpha across the blood-brain barrier in young ICR and young and aged SAMP8 mice. Neurobiology of Aging. 2001;22:671–676. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33:87–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

