Rec25 and Rec27, novel linear-element components, link cohesin to meiotic DNA breakage and recombination
- PMID: 18514516
- PMCID: PMC3119532
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.05.025
Rec25 and Rec27, novel linear-element components, link cohesin to meiotic DNA breakage and recombination
Abstract
Meiosis is a specialized nuclear division by which sexually reproducing diploid organisms generate haploid gametes. Recombination between homologous chromosomes facilitates accurate meiotic chromosome segregation and is initiated by DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) made by the conserved topoisomerase-like protein Spo11 (Rec12 in fission yeast), but DSBs are not evenly distributed across the genome. In Schizosaccharomyces pombe, proteinaceous structures known as linear elements (LinEs) are formed during meiotic prophase. The meiosis-specific cohesin subunits Rec8 and Rec11 are essential for DSB formation in some regions of the genome, as well as for formation of LinEs or the related synaptonemal complex (SC) in other eukaryotes. Proteins required for DSB formation decorate LinEs, and mutants lacking Rec10, a major component of LinEs, are completely defective for recombination. Although recombination may occur in the context of LinEs, it is not well understood how Rec10 is loaded onto chromosomes. We describe two novel components of LinEs in fission yeast, Rec25 and Rec27. Comparisons of rec25Delta, rec27Delta, and rec10Delta mutants suggest multiple pathways to load Rec10. In the major pathway, Rec10 is loaded, together with Rec25 and Rec27, in a Rec8-dependent manner with subsequent region-specific effects on recombination.
Figures
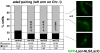
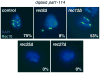

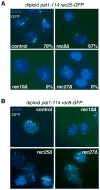
References
-
- Petronczki M, Siomos MF, Nasmyth K. Un menage a quatre: the molecular biology of chromosome segregation in meiosis. Cell. 2003;112:423–440. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997;88:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes MD, Farah JA, Smith GR. Meiotic DNA breaks associated with recombination in S. pombe. Mol Cell. 2000;5:883–888. - PubMed
-
- Romanienko PJ, Camerini-Otero RD. The mouse Spo11 gene is required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Mol Cell. 2000;6:975–987. - PubMed
-
- de Massy B. Distribution of meiotic recombination sites. Trends Genet. 2003;19:514–522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

