The morphologies of breast cancer cell lines in three-dimensional assays correlate with their profiles of gene expression
- PMID: 18516279
- PMCID: PMC2391005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2007.02.004
The morphologies of breast cancer cell lines in three-dimensional assays correlate with their profiles of gene expression
Abstract
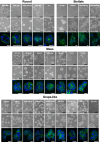
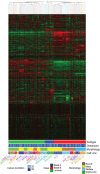
3D cell cultures are rapidly becoming the method of choice for the physiologically relevant modeling of many aspects of non-malignant and malignant cell behavior ex vivo. Nevertheless, only a limited number of distinct cell types have been evaluated in this assay to date. Here we report the first large scale comparison of the transcriptional profiles and 3D cell culture phenotypes of a substantial panel of human breast cancer cell lines. Each cell line adopts a colony morphology of one of four main classes in 3D culture. These morphologies reflect, at least in part, the underlying gene expression profile and protein expression patterns of the cell lines, and distinct morphologies were also associated with tumor cell invasiveness and with cell lines originating from metastases. We further demonstrate that consistent differences in genes encoding signal transduction proteins emerge when even tumor cells are cultured in 3D microenvironments.
Keywords: 3D culture; Breast cancer; extracellular matrix; gene expression profiling; signal transduction.
Figures



References
-
- Albini, A. , Iwamoto, Y. , Kleinman, H.K. , Martin, G.R. , Aaronson, S.A. , Kozlowski, J.M. , McEwan, R.N. , 1987. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Research. 47, 3239–3245. - PubMed
-
- Bellis, S.L. , 2004. Variant glycosylation: an underappreciated regulatory mechanism for beta1 integrins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1663, 52–60. - PubMed
-
- Bild, A.H. , Yao, G. , Chang, J.T. , Wang, Q. , Potti, A. , Chasse, D. , Joshi, M.B. , Harpole, D. , Lancaster, J.M. , Berchuck, A. , 2006. Oncogenic pathway signatures in human cancers as a guide to targeted therapies. Nature. 439, 353–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

