Eukaryotic DNA ligases: structural and functional insights
- PMID: 18518823
- PMCID: PMC2933818
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061306.123941
Eukaryotic DNA ligases: structural and functional insights
Abstract
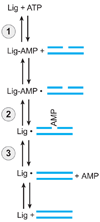
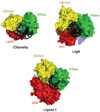
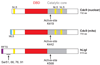
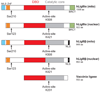
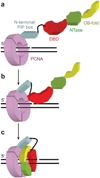
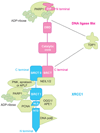
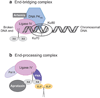
DNA ligases are required for DNA replication, repair, and recombination. In eukaryotes, there are three families of ATP-dependent DNA ligases. Members of the DNA ligase I and IV families are found in all eukaryotes, whereas DNA ligase III family members are restricted to vertebrates. These enzymes share a common catalytic region comprising a DNA-binding domain, a nucleotidyltransferase (NTase) domain, and an oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding (OB)-fold domain. The catalytic region encircles nicked DNA with each of the domains contacting the DNA duplex. The unique segments adjacent to the catalytic region of eukaryotic DNA ligases are involved in specific protein-protein interactions with a growing number of DNA replication and repair proteins. These interactions determine the specific cellular functions of the DNA ligase isozymes. In mammals, defects in DNA ligation have been linked with an increased incidence of cancer and neurodegeneration.
Figures
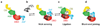

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

