MRI of pulmonary nodules: technique and diagnostic value
- PMID: 18519226
- PMCID: PMC2413430
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2008.0018
MRI of pulmonary nodules: technique and diagnostic value
Abstract
Chest wall invasion by a tumour and mediastinal masses are known to benefit from the superior soft tissue contrast of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, helical computed tomography (CT) (i.e. with multiple row detector systems) remains the modality of choice to detect and follow lesions of the lung parenchyma. Since minimizing radiation exposure plays a minor role in oncologic patients, there are only few routine indications for which MRI of lung parenchyma is preferred to CT. This includes whole body MR imaging for staging or scientific studies with frequent follow-up examinations. MR-based lung imaging in this context was always considered as a weak point. Depending on the sequence technique and imaging conditions (i.e. ability to hold breath) the threshold for lung nodule detection with MRI using 1.5 T systems was estimated to be above 3-4 mm. The feasibility of lung MRI at 0.3-0.5 T and 3.0 T systems has been demonstrated. The clinical value of time-resolved lung nodule perfusion analysis cannot yet be determined, although the combination of perfusion characteristics with morphologic criteria contributes to estimate the integrity of a solitary lesion.
Figures
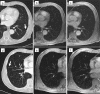
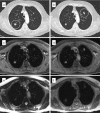
References
-
- Biederer J, Schoene A, Freitag S, Reuter M, Heller M. Simulated pulmonary nodules implanted in a dedicated porcine chest phantom: sensitivity of MR imaging for detection. Radiology. 2003;227:475–83. - PubMed
-
- Both M, Schultze J, Reuter M, et al. Fast T1- and T2-weighted pulmonary MR-imaging in patients with bronchial carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 2005;53:478–88. - PubMed
-
- Schroeder T, Ruehm SG, Debatin JF, Ladd ME, Barkhausen J, Goehde SC. Detection of pulmonary nodules using a 2D HASTE MR sequence: comparison with MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:979–84. - PubMed
-
- Bruegel M, Gaa J, Woertler K, et al. MRI of the lung: value of different turbo spin-echo, single-shot turbo spin-echo, and 3D gradient-echo pulse sequences for the detection of pulmonary metastases. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Puderbach M, Hintze C, Ley S, Eichinger M, Kauczor HU, Biederer J. MR imaging of the chest. A practical approach at 1.5 T. Eur J Radiol. 2007;64:345–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
