Beta1 integrin inhibition dramatically enhances radiotherapy efficacy in human breast cancer xenografts
- PMID: 18519702
- PMCID: PMC3719863
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6390
Beta1 integrin inhibition dramatically enhances radiotherapy efficacy in human breast cancer xenografts
Abstract
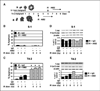
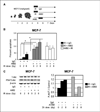
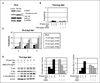
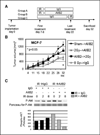
Beta(1) integrin signaling has been shown to mediate cellular resistance to apoptosis after exposure to ionizing radiation (IR). Other signaling molecules that increase resistance include Akt, which promotes cell survival downstream of beta(1) integrin signaling. We previously showed that beta(1) integrin inhibitory antibodies (e.g., AIIB2) enhance apoptosis and decrease growth in human breast cancer cells in three-dimensional laminin-rich extracellular matrix (lrECM) cultures and in vivo. Here, we asked whether AIIB2 could synergize with IR to modify Akt-mediated IR resistance. We used three-dimensional lrECM cultures to test the optimal combination of AIIB2 with IR treatment of two breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 and HMT3522-T4-2, as well as T4-2 myr-Akt breast cancer colonies or HMT3522-S-1, which form normal organotypic structures in three-dimensional lrECM. Colonies were assayed for apoptosis and beta(1) integrin/Akt signaling pathways were evaluated using Western blot. In addition, mice bearing MCF-7 xenografts were used to validate the findings in three-dimensional lrECM. We report that AIIB2 increased apoptosis optimally post-IR by down-regulating Akt in breast cancer colonies in three-dimensional lrECM. In vivo, addition of AIIB2 after IR significantly enhanced tumor growth inhibition and apoptosis compared with either treatment alone. Remarkably, the degree of tumor growth inhibition using AIIB2 plus 2 Gy radiation was similar to that of 8 Gy alone. We previously showed that AIIB2 had no discernible toxicity in mice; here, its addition allowed for a significant reduction in the IR dose that was necessary to achieve comparable growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer xenografts in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β1-Integrin via NF-κB signaling is essential for acquisition of invasiveness in a model of radiation treated in situ breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R60. doi: 10.1186/bcr3454. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23883667 Free PMC article.
-
Beta1 integrin inhibitory antibody induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells, inhibits growth, and distinguishes malignant from normal phenotype in three dimensional cultures and in vivo.Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 1;66(3):1526-35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3071. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16452209 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB regulates radioresistance mediated by β1-integrin in three-dimensional culture of breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 15;73(12):3737-48. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3537. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23576567 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous β1 integrin-EGFR targeting and radiosensitization of human head and neck cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Feb 5;107(2):dju419. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju419. Print 2015 Feb. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. PMID: 25663685
-
beta1 integrin targeting to enhance radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Biol. 2009 Nov;85(11):923-8. doi: 10.3109/09553000903232876. Int J Radiat Biol. 2009. PMID: 19895268 Review.
Cited by
-
β1 integrin: an emerging player in the modulation of tumorigenesis and response to therapy.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Mar-Apr;6(2):71-7. doi: 10.4161/cam.20077. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22568952 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-matrix interactions in mammary gland development and breast cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Oct;2(10):a003202. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003202. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20702598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast heterogeneity in the cancer wound.J Exp Med. 2014 Jul 28;211(8):1503-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140692. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25071162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D matrix-based cell cultures: Automated analysis of tumor cell survival and proliferation.Int J Oncol. 2016 Jan;48(1):313-21. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3230. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26549537 Free PMC article.
-
The pathobiology of collagens in glioma.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Oct;11(10):1129-40. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0236. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23861322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Park CC, Mitsumori M, Nixon A, et al. Outcome at 8 years after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for invasive breast cancer: influence of margin status and systemic therapy on local recurrence. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:1668–1675. - PubMed
-
- Barcellos-Hoff MH, Park C, Wright EG. Radiation and the microenvironment—tumorigenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:867–875. - PubMed
-
- Onoda JM, Piechocki MP, Honn KV. Radiation-induced increase in expression of the αIIbβ3 integrin in melanoma cells: effects on metastatic potential. Radiat Res. 1992;130:281–288. - PubMed
-
- Cordes N, Blaese MA, Meineke V, Van Beuningen D. Ionizing radiation induces up-regulation of functional β1-integrin in human lung tumour cell lines in vitro . Int J Radiat Biol. 2002;78:347–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

