Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4: regulation by thiazolidinediones and implication in glyceroneogenesis in adipose tissue
- PMID: 18519799
- PMCID: PMC2518477
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0477
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4: regulation by thiazolidinediones and implication in glyceroneogenesis in adipose tissue
Abstract
Objective: Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) serves as the metabolic switch between glucose and fatty acid utilization. PDC activity is inhibited by PDC kinase (PDK). PDC shares the same substrate, i.e., pyruvate, as glyceroneogenesis, a pathway controlling fatty acid release from white adipose tissue (WAT). Thiazolidinediones activate glyceroneogenesis. We studied the regulation by rosiglitazone of PDK2 and PDK4 isoforms and tested the hypothesis that glyceroneogenesis could be controlled by PDK.
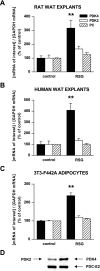
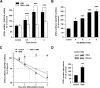
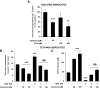
Research design and methods: Rosiglitazone was administered to Zucker fa/fa rats, and then PDK4 and PDK2 mRNAs were examined in subcutaneous, periepididymal, and retroperitoneal WAT, liver, and muscle by real-time RT-PCR. Cultured WAT explants from humans and rats and 3T3-F442A adipocytes were rosiglitazone-treated before analyses of PDK2 and PDK4 mRNA and protein. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) was transfected by electroporation. Glyceroneogenesis was determined using [1-(14)C]pyruvate incorporation into lipids.
Results: Rosiglitazone increased PDK4 mRNA in all WAT depots but not in liver and muscle. PDK2 transcript was not affected. This isoform selectivity was also found in ex vivo-treated explants. In 3T3-F442A adipocytes, Pdk4 expression was strongly and selectively induced by rosiglitazone in a direct and transcriptional manner, with a concentration required for half-maximal effect at 1 nmol/l. The use of dichloroacetic acid or leelamine, two PDK inhibitors, or a specific PDK4 siRNA demonstrated that PDK4 participated in glyceroneogenesis, therefore altering nonesterified fatty acid release in both basal and rosiglitazone-activated conditions.
Conclusions: These data show that PDK4 upregulation in adipocytes participates in the hypolipidemic effect of thiazolidinediones through modulation of glyceroneogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Boden G, Chen X, Stein TP: Gluconeogenesis in moderately and severely hyperglycemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280 :E23 –E30,2001 - PubMed
-
- Kelley DE, Mokan M, Mandarino LJ: Intracellular defects in glucose metabolism in obese patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 41 :698 –706,1992 - PubMed
-
- Eriksson JW, Smith U, Waagstein F, Wysocki M, Jansson PA: Glucose turnover and adipose tissue lipolysis are insulin-resistant in healthy relatives of type 2 diabetes patients: is cellular insulin resistance a secondary phenomenon? Diabetes 48 :1572 –1578,1999 - PubMed
-
- Gelding SV, Coldham N, Niththyananthan R, Anyaoku V, Johnston DG: Insulin resistance with respect to lipolysis in non-diabetic relatives of European patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 12 :66 –73,1995 - PubMed
-
- Charles MA, Eschwege E, Thibult N, Claude JR, Warnet JM, Rosselin GE, Girard J, Balkau B: The role of non-esterified fatty acids in the deterioration of glucose tolerance in Caucasian subjects: results of the Paris Prospective Study. Diabetologia 40 :1101 –1106,1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

