Long-term remission of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from matched sibling donors: a 20-year experience with the fractionated total body irradiation-etoposide regimen
- PMID: 18519812
- PMCID: PMC2481551
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-143115
Long-term remission of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from matched sibling donors: a 20-year experience with the fractionated total body irradiation-etoposide regimen
Abstract
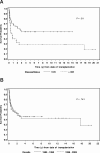
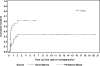
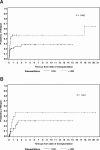
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is the only known curative modality for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph(+) ALL). Sixty-seven patients with HLA-matched sibling donors received fractionated total body irradiation (FTBI) and high-dose VP16, whereas 11 patients received FTBI/VP16/cyclophosphamide, and 1 patient received FTBI/VP16/busulfan. The median age was 36 years. At the time of HCT, 49 patients (62%) were in first complete remission (CR1) and 30 patients (38%) were beyond CR1 (> CR1). The median follow-up was 75 months (range, 14-245 months). The 10-year overall survival for the CR1 and beyond CR1 patients was 54% and 29% (P = .01), respectively, and event-free survival was 48% and 26% (P = .02), respectively. There was no significant difference in relapse incidence (28% vs 41%, P = .28), but nonrelapse mortality was significantly higher in the beyond CR1 patients, (31% vs 54%, P = .03, respectively). By univariate analysis, factors affecting event-free and overall survival were white blood cell count at diagnosis (< 30 x 10(9)/L vs > 30 x 10(9)/L) and disease status (CR1 vs > CR1). The median time to relapse for CR1 and for beyond CR1 patients was 12 months and 9 months, respectively. Our results indicate that FTBI/VP16 with or without cyclophosphamide confers long-term survival in Ph(+) ALL patients and that disease status at the time of HCT is an important predictor of outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Cytogenetic abnormalities in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: correlations with hematologic findings outcome: a Collaborative Study of the Group Francais de Cytogenetique Hematologique. Blood. 1996;87:3135–3142. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Kim DW, Cho B, et al. Risk factors for adults with Philadelphia-chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in remission treated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: the potential of real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Br J Haematol. 2003;120:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Yanada M, Naoe T, Iida H, et al. Myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: significant roles of total body irradiation and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005;36:867–872. - PubMed
-
- Esperou H, Boiron JM, Cayuela JM, et al. A potential graft-versus-leukemia effect after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results from the French Bone Marrow Transplantation Society. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003;31:909–918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

