Plasma pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine after controlled oral administration to young adults
- PMID: 18520604
- PMCID: PMC2663855
- DOI: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e3181684fa0
Plasma pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine after controlled oral administration to young adults
Abstract
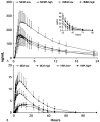
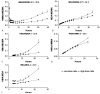
This study examines the plasma pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and metabolites 4-hydroxy-3-methoxymethamphetamine (HMMA), 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyamphetamine (HMA) in young adults for up to 143 hours after drug administration. Seventeen female and male participants (black, white, and Hispanic) received placebo, low (1.0 mg/kg), and high (1.6 mg/kg) oral MDMA doses (comparable to recreational doses) in a double-blind, randomized, balanced, within-subject design while residing on a closed research unit. Doses were separated by 1 week or more. A fully validated two-dimensional gas chromatography/mass spectrometry method simultaneously quantified MDMA, HMMA, MDA, and HMA. Calibration curves were MDA, 1 to 100 ng/mL; HMA, 2.5 to 100 ng/mL; and MDMA and HMMA, 2.5 to 400 ng/mL. Mean +/- standard deviation maximum plasma concentrations (C(max)) of 162.9 +/- 39.8 and 171.9 +/- 79.5 ng/mL were observed for MDMA and HMMA, respectively, after low-dose MDMA. After the high dose, mean MDMA Cmax significantly increased to 291.8 +/- 76.5 ng/mL, whereas mean HMMA C(max) was unchanged at 173.5 +/- 66.3 ng/mL. High intersubject variability in C(max) was observed. Mean MDA C(max) were 8.4 +/- 2.1 (low) and 13.8 +/- 3.8 (high) ng/mL. HMA Cmax were 3.5 +/- 0.4 and 3.9 +/- 0.9 ng/mL after the low and high doses, respectively. AUC infinity displayed similar trends to C(max), demonstrating nonlinear pharmacokinetics. Times of last plasma detection were generally HMA < MDA < MDMA < HMMA. Mean half-lives (t1/2) of MDMA, MDA, and HMMA were approximately 7 to 8 hours, 10.5 to 12.5 hours, and 11.5 to 13.5 hours, respectively. HMA t1/2 showed high variability. Mean MDMA volume of distribution was constant for low and high doses; clearance was significantly higher after the low dose. This study presents MDMA plasma pharmacokinetic data for the first time from blacks and females as well as measurement of HMMA and HMA concentrations after low and high MDMA doses and more frequent and extended plasma sampling than in prior studies.
Figures



References
-
- Pentney AR. An exploration of the history and controversies surrounding MDMA and MDA. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2001;33:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Sumnall HR, Cole JC, Jerome L. The varieties of ecstatic experience: an exploration of the subjective experiences of ecstasy. J Psychopharmacol. 2006;20:670–682. - PubMed
-
- Greer G, Tolbert R. Subjective reports of the effects of MDMA in a clinical setting. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1986;18:319–327. - PubMed
-
- Downing J. The psychological and physiological effects of MDMA on normal volunteers. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1986;18:335–340. - PubMed
-
- Vollenweider FX, Gamma A, Liechti M, et al. Psychological and cardiovascular effects and short-term sequelae of MDMA (‘ecstasy’) in MDMA-naive healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1998;19:241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

