Concomitant TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology is present in Alzheimer disease and corticobasal degeneration but not in other tauopathies
- PMID: 18520774
- PMCID: PMC3659339
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e31817713b5
Concomitant TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology is present in Alzheimer disease and corticobasal degeneration but not in other tauopathies
Abstract
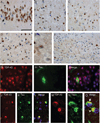
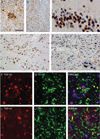
Pathologic TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) is a disease protein in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions (FTLD-U) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. We studied the presence, frequency, and distribution of TDP-43 pathology by immunohistochemistry and biochemistry in a series of clinically well-characterized tauopathy patient brains, including 182 Alzheimer disease (AD), 39 corticobasal degeneration, 77 progressive supranuclear palsy, and 12 Pick disease cases and investigated the clinical impact of concomitant TDP-43 pathology in these cases. TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology was found in 25.8% of AD cases. It was restricted to the dentate gyrus and entorhinal cortex in approximately 75% of cases; approximately 25% showed more widespread TDP-43 pathology in frontal and temporal cortices, resembling the FTLD-U subtype associated with progranulin mutations. TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology in AD was associated with significantly longer disease duration, but there was no association with the clinical presentation (148 cases diagnosed as AD and 34 cases diagnosed as frontotemporal lobar degeneration). Progressive supranuclear palsy and Pick disease cases showed no TDP-43 inclusions and no biochemical alterations of TDP-43. There was, however, a unique, predominantly glial TDP-43 pathology with staining of astrocytic plaque-like structures and coiled bodies in 15.4% of corticobasal degeneration cases; this was associated with biochemical TDP-43 changes similar to those in FTLD-U. These findings provide further insight into the burden and clinical significance of TDP-43 pathology in disorders other than FTLD-U and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Figures

References
-
- Grossman M. Frontotemporal dementia: A review. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2002;8:566–583. - PubMed
-
- Shi J, Shaw CL, Du Plessis D, et al. Histopathological changes underlying frontotemporal lobar degeneration with clinicopathological correlation. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2005;110:501–512. - PubMed
-
- Lipton AM, White CL, 3rd, Bigio EH. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease-type inclusions predominates in 76 cases of frontotemporal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2004;108:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Johnson JK, Diehl J, Mendez MF, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: Demographic characteristics of 353 patients. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:925–930. - PubMed
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314:130–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

