Hypertension and cerebrovascular dysfunction
- PMID: 18522829
- PMCID: PMC2475602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.03.010
Hypertension and cerebrovascular dysfunction
Abstract
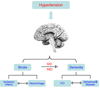
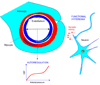
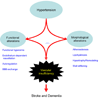
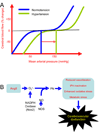
Essential hypertension has devastating effects on the brain, being the major cause of stroke and a leading cause of dementia. Hypertension alters the structure of cerebral blood vessels and disrupts intricate vasoregulatory mechanisms that assure an adequate blood supply to the brain. These alterations threaten the cerebral blood supply and increase the susceptibility of the brain to ischemic injury as well as Alzheimer's disease. This review focuses on the mechanisms by which hypertension disrupts cerebral blood vessels, highlighting recent advances and outstanding issues.
Figures
References
-
- Ago T, Kitazono T, Kuroda J, Kumai Y, Kamouchi M, Ooboshi H, Wakisaka M, Kawahara T, Rokutan K, Ibayashi S, et al. NAD(P)H oxidases in rat basilar arterial endothelial cells. Stroke. 2005;36:1040–1046. - PubMed
-
- Andresen J, Shafi NI, Bryan RM., Jr Endothelial influences on cerebrovascular tone. J Appl Physiol. 2006;100:318–327. - PubMed
-
- Barry DI. Cerebral blood flow in hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7 Suppl 2:S94–S98. - PubMed
-
- Baumbach GL, Didion SP, Faraci FM. Hypertrophy of cerebral arterioles in mice deficient in expression of the gene for CuZn superoxide dismutase. Stroke. 2006;37:1850–1855. - PubMed
-
- Baumbach GL, Heistad DD. Cerebral circulation in chronic arterial hypertension. Hypertension. 1988;12:89–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

