ATP is released by monocytes stimulated with pathogen-sensing receptor ligands and induces IL-1beta and IL-18 secretion in an autocrine way
- PMID: 18523012
- PMCID: PMC2430360
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0709684105
ATP is released by monocytes stimulated with pathogen-sensing receptor ligands and induces IL-1beta and IL-18 secretion in an autocrine way
Abstract
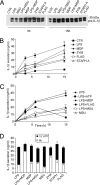
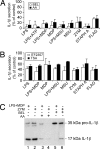
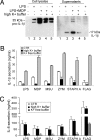
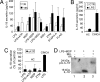
IL-1beta and IL-18 are crucial mediators of inflammation, and a defective control of their release may cause serious diseases. Yet, the mechanisms regulating IL-1beta and IL-18 secretion are partially undefined. Both cytokines are produced as inactive cytoplasmic precursors. Processing to the active form is mediated by caspase-1, which is in turn activated by the multiprotein complex inflammasome. Here, we show that in primary human monocytes microbial components acting on different pathogen-sensing receptors and the danger-associated molecule uric acid are all competent to induce maturation and secretion of IL-1beta and IL-18 through a process that involves as a first event the extracellular release of endogenous ATP. ATP release is followed by autocrine stimulation of the purinergic receptors P2X(7). Indeed, antagonists of the P2X(7) receptor (P2X(7)R), or treatment with apyrase, prevent IL-1beta and IL-18 maturation and secretion triggered by the different stimuli. At variance, blocking P2X(7)R activity has no effects on IL-1beta secretion by monocytes carrying a mutated inflammasome that does not require exogenous ATP for activation. P2X(7)R engagement is followed by K+ efflux and activation of phospholipase A(2). Both events are required for processing and secretion induced by all of the stimuli. Thus, stimuli acting on different pathogen-sensing receptors converge on a common pathway where ATP externalization is the first step in the cascade of events leading to inflammasome activation and IL-1beta and IL-18 secretion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
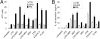
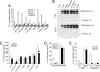
References
-
- Kaczorowski DJ, Mollen KP, Edmonds R, Billiar TR. Early events in the recognition of danger signals after tissue injury. J Leukocyte Biol. 2008;83:546–552. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell JA, Paul-Clark MJ, Clarke GW, McMaster SK, Cartwright N. Critical role of toll-like receptors and nucleotide oligomerization domain in the regulation of health and disease. J Endocrinol. 2007;193:323–330. - PubMed
-
- Rubartelli A, Lotze MT. Inside, outside, upside down: Damage-associated molecular-pattern molecules (DAMPs) and redox. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:429–436. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1, interleukin-1 receptors, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16:457–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

