Label-free and dynamic detection of biomolecular interactions for high-throughput microarray applications
- PMID: 18523019
- PMCID: PMC2430348
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711421105
Label-free and dynamic detection of biomolecular interactions for high-throughput microarray applications
Abstract
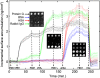
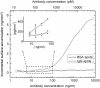
Direct monitoring of primary molecular-binding interactions without the need for secondary reactants would markedly simplify and expand applications of high-throughput label-free detection methods. A simple interferometric technique is presented that monitors the optical phase difference resulting from accumulated biomolecular mass. As an example, 50 spots for each of four proteins consisting of BSA, human serum albumin, rabbit IgG, and protein G were dynamically monitored as they captured corresponding antibodies. Dynamic measurements were made at 26 pg/mm(2) SD per spot and with a detectable concentration of 19 ng/ml. The presented method is particularly relevant for protein microarray analysis because it is label-free, simple, sensitive, and easily scales to high-throughput.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
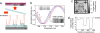
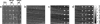
References
-
- Engvall E, Perlman P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971;8:871–874. - PubMed
-
- Gershoni JM, Palade GE. Protein blotting: Principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983;131:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P. A perspective on protein microarrays. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:225–229. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran N, Larson DN, Stark PRH, Hainsworth E, LaBaer J. Emerging tools for real-time label-free detection of interactions on functional protein microarrays. FEBS J. 2005;272:5412–5425. - PubMed
-
- Homola J, Vaisocherova H, Dostalek J, Piliarik M. Multi-analyte surface Plasmon resonance biosensing. Methods. 2005;37:25–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

