Axonal injury and regeneration in the adult brain of Drosophila
- PMID: 18524906
- PMCID: PMC2693324
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0101-08.2008
Axonal injury and regeneration in the adult brain of Drosophila
Abstract
Drosophila melanogaster is a leading genetic model system in nervous system development and disease research. Using the power of fly genetics in traumatic axonal injury research will significantly speed up the characterization of molecular processes that control axonal regeneration in the CNS. We developed a versatile and physiologically robust preparation for the long-term culture of the whole Drosophila brain. We use this method to develop a novel Drosophila model for CNS axonal injury and regeneration. We first show that, similar to mammalian CNS axons, injured adult wild-type fly CNS axons fail to regenerate, whereas adult-specific enhancement of protein kinase A activity increases the regenerative capacity of lesioned neurons. Combined, these observations suggest conservation of neuronal regeneration mechanisms after injury. We next exploit this model to explore pathways that induce robust regeneration and find that adult-specific activation of c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling is sufficient for de novo CNS axonal regeneration injury, including the growth of new axons past the lesion site and into the normal target area.
Figures
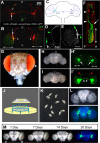



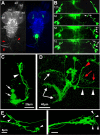
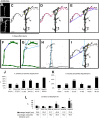
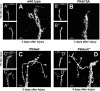

References
-
- Adachi-Yamada T, Fujimura-Kamada K, Nishida Y, Matsumoto K. Distortion of proximodistal information causes JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila wing. Nature. 1999;400:166–169. - PubMed
-
- Belenky M, Wagner S, Yarom Y, Matzner H, Cohen S, Castel M. The suprachiasmatic nucleus in stationary organotypic culture. Neuroscience. 1996;70:127–143. - PubMed
-
- Bier E. Drosophila, the golden bug, emerges as a tool for human genetics. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:9–23. - PubMed
-
- Bilen J, Bonini NM. Drosophila as a model for human neurodegenerative disease. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:153–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
