Characteristics of carbohydrate antigen binding to the presentation protein HLA-DR
- PMID: 18525076
- PMCID: PMC2733769
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwn050
Characteristics of carbohydrate antigen binding to the presentation protein HLA-DR
Abstract
Zwitterionic polysaccharide antigens (ZPSs) were recently shown to activate T cells in a class II major histocompatibility complex (MHCII)-dependent fashion requiring antigen presenting cell (APC)-mediated oxidative processing although little is known about the mechanism or affinity of carbohydrate presentation (Cobb BA, Wang Q, Tzianabos AO, Kasper DL. 2004. Polysaccharide processing and presentation by the MHCII pathway. Cell. 117:677-687). A recent study showed that the helical conformation of ZPSs (Wang Y, Kalka-Moll WM, Roehrl MH, Kasper DL. 2000. Structural basis of the abscess-modulating polysaccharide A2 from Bacteroides fragilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:13478-13483; Choi YH, Roehrl MH, Kasper DL, Wang JY. 2002. A unique structural pattern shared by T-cell-activating and abscess-regulating zwitterionic polysaccharides. Biochemistry. 41:15144-15151) is closely linked with immunogenic activity (Tzianabos AO, Onderdonk AB, Rosner B, Cisneros RL, Kasper DL. 1993. Structural features of polysaccharides that induce intra-abdominal abscesses. Science. 262:416-419) and is stabilized by a zwitterionic charge motif (Kreisman LS, Friedman JH, Neaga A, Cobb BA. 2007. Structure and function relations with a T-cell-activating polysaccharide antigen using circular dichroism. Glycobiology. 17:46-55), suggesting a strong carbohydrate structure-function relationship. In this study, we show that PSA, the ZPS from Bacteroides fragilis, associates with MHCII at high affinity and 1:1 stoichiometry through a mechanism mirroring peptide presentation. Interestingly, PSA binding was mutually exclusive with common MHCII antigens and showed significant allelic differences in binding affinity. The antigen exchange factor HLA-DM that catalyzes peptide antigen association with MHCII also increased the rate of ZPS association and was required for APC presentation and ZPS-mediated T cell activation. Finally, the zwitterionic nature of these antigens was required only for MHCII binding, and not endocytosis, processing, or vesicular trafficking to MHCII-containing vesicles. This report is the first quantitative analysis of the binding mechanism of carbohydrate antigens with MHCII and leads to a novel model for nontraditional MHCII antigen presentation during bacterial infections.
Figures


 ) is the moles ligand bound per mole of MHCII; thus, the Bmax represents the stoichiometry. All data points represent the average of at least four replicates. PSA saturably binds to DR1 (panel B; Kd = 1.9 ± 0.4 μM; Bmax = 0.8 ± 0.08), DR2 (panel C; Kd = 0.31 ± 0.05 μM; Bmax = 1.0 ± 0.04), and DR4 (panel D; Kd = 1.0 ± 0.3 μM; Bmax = 1.0 ± 0.1). Control binding with SEA (E) and MBPp (F) with DR2 show Kd values of 4.7 ± 2.0 μM and 4.3 ± 2.6 μM with Bmax values of 1.5 ± 0.5 and 1.2 ± 0.2, respectively.
) is the moles ligand bound per mole of MHCII; thus, the Bmax represents the stoichiometry. All data points represent the average of at least four replicates. PSA saturably binds to DR1 (panel B; Kd = 1.9 ± 0.4 μM; Bmax = 0.8 ± 0.08), DR2 (panel C; Kd = 0.31 ± 0.05 μM; Bmax = 1.0 ± 0.04), and DR4 (panel D; Kd = 1.0 ± 0.3 μM; Bmax = 1.0 ± 0.1). Control binding with SEA (E) and MBPp (F) with DR2 show Kd values of 4.7 ± 2.0 μM and 4.3 ± 2.6 μM with Bmax values of 1.5 ± 0.5 and 1.2 ± 0.2, respectively.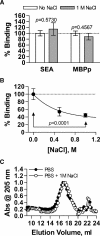





Similar articles
-
Zwitterionic polysaccharides stimulate T cells by MHC class II-dependent interactions.J Immunol. 2002 Dec 1;169(11):6149-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.11.6149. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12444118
-
Microbial carbohydrate depolymerization by antigen-presenting cells: deamination prior to presentation by the MHCII pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 1;105(13):5183-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800974105. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18381820 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide processing and presentation by the MHCII pathway.Cell. 2004 May 28;117(5):677-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.05.001. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15163414 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational variation in structures of classical and non-classical MHCII proteins and functional implications.Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):144-57. doi: 10.1111/imr.12003. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of HLA-DM induced peptide exchange in the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway.Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Feb;24(1):105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22138314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carbohydrates and T cells: a sweet twosome.Semin Immunol. 2013 Apr;25(2):146-51. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23757291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of the Capsular Polysaccharide A from Bacteroides fragilis with DC-SIGN on Human Dendritic Cells is Necessary for Its Processing and Presentation to T Cells.Front Immunol. 2013 May 6;4:103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00103. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23653626 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of gut-derived CD39 regulatory T cells in CNS demyelinating disease.Transl Res. 2017 Jan;179:126-138. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.07.016. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 27519147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mgat2 ablation in the myeloid lineage leads to defective glycoantigen T cell responses.Glycobiology. 2014 Mar;24(3):262-71. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwt107. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Glycobiology. 2014. PMID: 24310166 Free PMC article.
-
The Gut Microbiome and Multiple Sclerosis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018 Jun 1;8(6):a029017. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029017. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018. PMID: 29311123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pober JS. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. 4th ed. New York: W.B. Saunders; 2000.
-
- Babbitt BP, Allen PM, Matsueda G, Haber E, Unanue ER. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1985;317:359–361. - PubMed
-
- Baumann H, Tzianabos AO, Brisson JR, Kasper DL, Jennings HJ. Structural elucidation of two capsular polysaccharides from one strain of Bacteroides fragilis using high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992;31:4081–4089. - PubMed
-
- Boitel B, Ermonval M, Panina-Bordignon P, Mariuzza RA, Lanzavecchia A, Acuto O. Preferential V beta gene usage and lack of junctional sequence conservation among human T cell receptors specific for a tetanus toxin-derived peptide: Evidence for a dominant role of a germline-encoded V region in antigen/major histocompatibility complex recognition. J Exp Med. 1992;175:765–777. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brubaker JO, Li Q, Tzianabos AO, Kasper DL, Finberg RW. Mitogenic activity of purified capsular polysaccharide A from Bacteroides fragilis: Differential stimulatory effect on mouse and rat lymphocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1999;162:2235–2242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

