Etiopathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- PMID: 18528932
- PMCID: PMC2716589
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.3350
Etiopathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
Abstract
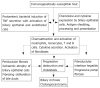
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic cholestatic liver disease of unknown etiology but lymphocytic portal tract infiltration is suggestive of an immune-mediated basis for this disease. Associations with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) especially ulcerative colitis (UC), and with particular autoimmune diseases, as well as the genetic associations further suggest PSC may be an immune-mediated disease. The immunogenetics of PSC have been the subject of active research and several HLA and non-HLA associated genes have been implicated in the development of the disease. Lymphocytes derived from the inflamed gut may enter the liver via the enterohepatic circulation to cause hepatic disease. PSC may be triggered in genetically susceptible individuals by infections or toxins entering the portal circulation through a permeable colon and hence evoking an abnormal immune response.
Figures
References
-
- Worthington J, Cullen S, Chapman R. Immunopathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2005;28:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Aadland E, Schrumpf E, Fausa O, Elgjo K, Heilo A, Aakhus T, Gjone E. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: a long-term follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987;22:655–664. - PubMed
-
- Broome U, Bergquist A. Primary sclerosing cholangitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and colon cancer. Semin Liver Dis. 2006;26:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Saarinen S, Olerup O, Broome U. Increased frequency of autoimmune diseases in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3195–3199. - PubMed
-
- Levy C, Lindor KD. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: epidemiology, natural history, and prognosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2006;26:22–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials