LTR retrotransposons and the evolution of dosage compensation in Drosophila
- PMID: 18533037
- PMCID: PMC2443393
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-55
LTR retrotransposons and the evolution of dosage compensation in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: Dosage compensation in Drosophila is the epigenetic process by which the expression of genes located on the single X-chromosome of males is elevated to equal the expression of X-linked genes in females where there are two copies of the X-chromosome. While epigenetic mechanisms are hypothesized to have evolved originally to silence transposable elements, a connection between transposable elements and the evolution of dosage compensation has yet to be demonstrated.
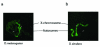
Results: We show that transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster copia LTR (long terminal repeat) retrotransposon is significantly down regulated when in the hemizygous state. DNA digestion and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses demonstrate that this down regulation is associated with changes in chromatin structure mediated by the histone acetyltransferase, MOF. MOF has previously been shown to play a central role in the Drosophila dosage compensation complex by binding to the hemizygous X-chromosome in males.
Conclusion: Our results are consistent with the hypothesis that MOF originally functioned to silence retrotransposons and, over evolutionary time, was co-opted to play an essential role in dosage compensation in Drosophila.
Figures
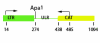

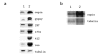

Similar articles
-
The non-dosage compensated Lsp1alpha gene of Drosophila melanogaster escapes acetylation by MOF in larval fat body nuclei, but is flanked by two dosage compensated genes.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 May 19;8:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-35. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17511883 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):367-75. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80431-1. Mol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10882077
-
Interelement selection in the regulatory region of the copia retrotransposon.J Mol Evol. 1998 Dec;47(6):670-6. doi: 10.1007/pl00006425. J Mol Evol. 1998. PMID: 9847408
-
Dosage dependent gene regulation and the compensation of the X chromosome in Drosophila males.Genetica. 2003 Mar;117(2-3):179-90. doi: 10.1023/a:1022935927763. Genetica. 2003. PMID: 12723697 Review.
-
LTR-retrotransposons in plants: Engines of evolution.Gene. 2017 Aug 30;626:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.04.051. Epub 2017 May 2. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28476688 Review.
Cited by
-
A surrogate approach to study the evolution of noncoding DNA elements that organize eukaryotic genomes.J Hered. 2009 Sep-Oct;100(5):624-36. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esp063. Epub 2009 Jul 27. J Hered. 2009. PMID: 19635763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C. elegans RNA-dependent RNA polymerases rrf-1 and ego-1 silence Drosophila transgenes by differing mechanisms.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Apr;70(8):1469-81. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1218-8. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23224429 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Recent Evolution of LTR Retrotransposons Drives Rice Genome Evolution During the Speciation of AA-Genome Oryza Species.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Jun 7;7(6):1875-1885. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.037572. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28413161 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione s-transferase omega 1 activity is sufficient to suppress neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of Parkinson disease.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6628-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.291179. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22219196 Free PMC article.
-
Population and clinical genetics of human transposable elements in the (post) genomic era.Mob Genet Elements. 2017 Jan 11;7(1):1-20. doi: 10.1080/2159256X.2017.1280116. eCollection 2017. Mob Genet Elements. 2017. PMID: 28228978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coffin JM, Hughes JM, Varmus HE. Retroviruses. Plainview: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

