Adeno-tonsillar surgery in Italy
- PMID: 18533547
- PMCID: PMC2640065
Adeno-tonsillar surgery in Italy
Abstract
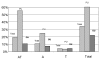
Indications to surgery for adeno-tonsillar inflammatory disorders and analysis of the effectiveness of surgical treatment, compared with watchful waiting strategy, continue to be the subject of scientific debate. The present investigation focuses on the surgical activity of 14 Italian Otorhinolaryngological Units between 1999 and 2004. Surgical interventions (adeno-tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy, tonsillectomy) on 26915 children (age range: 2-11 years) were considered. Data on adeno-tonsillar interventions were analysed in relation to other interventions of ENT interest, performed in the same units and in the same period. Adeno-tonsillar interventions accounted for 35.4% of all operations of ENT interest. Adeno-tonsillectomy accounted for 56.6% of overall adeno-tonsillar operations, adenoidectomy 31.6%, tonsillectomy 11.8%. The percentage for the three interventions was homogeneous in the period of the study and in the recruited units. The percentage of children who underwent adeno-tonsillar surgery in paediatric units was higher as compared to general units, as far as concerns the overall number of operations performed. In southern Italy, the number of adeno-tonsillar interventions, in general, and of adeno-tonsillectomy, in particular, was higher compared to that in northern Italy. Results of the present study suggest that environmental factors, cultural issues and local health demands, may influence indications and, therefore, the different incidence of the operations under consideration in the units taking part in the investigation.
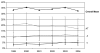
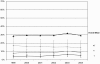
Le indicazioni al trattamento chirurgico nella patologia delle tonsille palatine e delle vegetazioni adenoidi continuano a sollecitare un vivace dibattito scientifico. La nostra ricerca ha riguardato l’attività chirurgica di 14 Centri specialistici otorinolaringoiatrici; sono stati presi in considerazione 26.915 pazienti, con età compresa fra i 2 e gli 11 anni, sottoposti ad interventi chirurgici faringei (adeno-tonsillectomia, adenoidectomia e tonsillectomia), nell’arco di tempo compreso fra il 1999 ed il 2004, per una patologia infiammatoria tonsillare e/o adenoidea; i dati relativi a questi pazienti sono stati analizzati tenendo conto degli altri interventi di interesse specialistico, eseguiti negli stessi Centri e nello stesso periodo. Gli interventi faringei costituiscono il 35,4% delle operazioni di competenza specialistica; le adenotonsillectomie incidono sul numero totale di operazioni faringee per il 56,6%, le adenoidectomie per il 31,6% e le tonsillectomie per il 11,8%. L’andamento delle percentuali medie, per i tre interventi, negli anni considerati, è omogeneo; vi è, però, una tendenza alla riduzione delle adenotonsillectomie con un corrispondente aumento degli altri due interventi. Nei Centri che operano in Ospedali Pediatrici il numero percentuale di casi sottoposto ad interventi faringei, in relazione al numero totale di operazioni, è nettamente superiore. Nel meridione d’Italia, il numero degli interventi faringei in generale e quello delle adeno-tonsillectomie in particolare, è più elevato, rispetto al settentrione. I dati raccolti nei singoli Centri, però, si discostano, talora, dalle medie per quanto riguarda sia l’andamento delle percentuali degli interventi negli anni oggetto dello studio, sia l’incidenza reciproca delle tre operazioni faringee studiate. I risultati del nostro studio e le osservazioni riportate in letteratura fanno presumere che fattori socio-ambientali, oltre che indirizzi culturali ed esigenze sanitarie locali, possano influenzare le indicazioni e la diversa incidenza degli interventi studiati.
Figures











References
-
- Rosefsky JB. Tonsillectomies and adenotonsillectomies. Will the debate never be over? Pediatrics 2003;112:205. - PubMed
-
- Paradise JL. Effectiveness of tonsillectomy depends on stringency of indications. Electronic letter 2005; http://adcbmjjournals.com/cgi/letters. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paradise JL, Bluestone CD, Bachman RZ, Colborn DK, Bernard BS, Taylor FH, et al. Efficacy of tonsillectomy for recurrent throat infection in severely affected children: results of parallel randomized and nonrandomized clinical trials. N Engl J Med 1984;310:674-83. - PubMed
-
- Baglio G, Bellussi L, Calia V, Canonico D, Denuccio C, De Vincentiis M, et al. Programma Nazionale sulle Linee Guida (PNLG4). Appropriatezza clinica e organizzativa degli interventi di tonsillectomia e/o adenoidectomia. Documento d’indirizzo (Isituto Superiore di Sanità): aprile 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
