Obesity prevalence from a European perspective: a systematic review
- PMID: 18533989
- PMCID: PMC2441615
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-200
Obesity prevalence from a European perspective: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Obesity has been recognised as an important contributing factor in the development of various diseases, but comparative data on this condition are limited. We therefore aimed to identify and discuss current epidemiological data on the prevalence of obesity in European countries.
Methods: We identified relevant published studies by means of a MEDLINE search (1990-2008) supplemented by information obtained from regulatory agencies. We only included surveys that used direct measures of weight and height and were representative of each country's overall population.
Results: In Europe, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index > or = 30 kg/m2) in men ranged from 4.0% to 28.3% and in women from 6.2% to 36.5%. We observed considerable geographic variation, with prevalence rates in Central, Eastern, and Southern Europe being higher than those in Western and Northern Europe.
Conclusion: In Europe, obesity has reached epidemic proportions. The data presented in our review emphasise the need for effective therapeutic and preventive strategies.
Figures
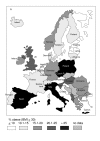
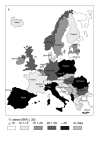
References
-
- Dusch von TK. Lehrbuch der Herzkrankheiten. Leipzig, Engelmann Verlag; 1868.
-
- Gikas A, Sotiropoulos A, Panagiotakos D, Peppas T, Skliros E, Pappas S. Prevalence, and associated risk factors, of self-reported diabetes mellitus in a sample of adult urban population in Greece: MEDICAL Exit Poll Research in Salamis (MEDICAL EXPRESS 2002) BMC Public Health. 2004;4:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-4-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heitmann BL. [Occurrence and development of overweight and obesity among adult Danes aged 30-60 years] Ugeskr Laeger. 1999;161:4380–4384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

